Effects of Combined Application of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Zoledronic Acid on Bone Mineral Density, Bone Metabolism, NPY and PGE2 in Elderly Patients with Osteoporotic Lumbar Vertebral Compression Fracture
- PMID: 38826002
- PMCID: PMC11145314
Effects of Combined Application of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Zoledronic Acid on Bone Mineral Density, Bone Metabolism, NPY and PGE2 in Elderly Patients with Osteoporotic Lumbar Vertebral Compression Fracture
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of the combined application of percutaneous vertebroplasty and zoledronic acid on bone mineral density (BMD), bone metabolism, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in elderly patients with osteoporotic lumbar vertebral compression fracture (OVCF).
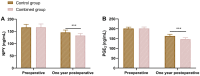
Methods: The medical records of 118 elderly patients with OVCF who received treatment at our hospital from March 2018 to March 2020 were collected and analyzed retrospectively. Vertebral body height, spinal function, pain degree, and lumbar BMD were compared between the two groups upon admission and three years after the operation. Additionally, the levels of bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (BALP), 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-(OH)D), beta collagen degradation fragments (β-CTx), neuropeptide Y (NPY), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the two groups were measured at admission and three years after the operation. Furthermore, complications in the two groups within three years after the operation were documented.
Results: After three years post-operation, the combination group showed a significantly greater improvement in vertebral body height compared to the control group (P<0.05). Moreover, the combination group exhibited a significantly lower Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) score compared to the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion: In elderly patients with OVCF, the combined use of zoledronic acid and percutaneous vertebroplasty is effective in improving lumbar function, BMD, and bone metabolism indices, while reducing pain and the levels of NPY and PGE2.
Keywords: Bone Metabolism; Osteoporotic Lumbar Vertebral Compression Fracture; Percutaneous Vertebroplasty; Zoledronic Acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
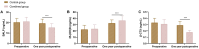
Similar articles
-
[Clinical application of zoledronic acid combined with vitamin K2 in percutaneous vertebroplasty for multi-segment osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020 Sep 25;33(9):820-6. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2020.09.006. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020. PMID: 32959568 Chinese.
-
Clinical Efficacy Analysis of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty Combined with Zoledronic Acid in the Treatment and Prevention of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.J Invest Surg. 2018 Oct;31(5):425-430. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2017.1339151. Epub 2017 Aug 22. J Invest Surg. 2018. PMID: 28829670 Clinical Trial.
-
Percutaneous kyphoplasty combined with zoledronic acid infusion in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures in the elderly.Clin Interv Aging. 2018 May 4;13:853-861. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S146871. eCollection 2018. Clin Interv Aging. 2018. PMID: 29765210 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Combined with Zoledronic Acid in Treatment and Prevention of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies.World Neurosurg. 2022 Jan;157:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.09.131. Epub 2021 Oct 14. World Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 34655820
-
Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Zoledronic Acid Combined with PVP/PKP in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 8;2021:6650358. doi: 10.1155/2021/6650358. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33928158 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical and biochemical efficacy zoledronic acid and denosumab combination: focus serum inflammatory factor level (serum ifcs), bone gla protein (bgp), and bone turnover markers b-collagen degradation product (b-ctx), and procollagen type 1 n-terminal propeptide (p1np).J Med Biochem. 2025 Jun 13;44(3):587-594. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-51444. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40821653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsoof D, Anderson G, McDonald CL, Basques B, Kuris E, Daniels AH. Diagnosis and Management of Vertebral Compression Fracture. Am J Med. 2022;135:815–821. - PubMed
-
- European Prospective Osteoporosis Study G. Felsenberg D, Silman AJ, Lunt M, Armbrecht G, Ismail AA, Finn JD, Cockerill WC, Banzer D, Benevolenskaya LI, Bhalla A, Bruges Armas J, Cannata JB, Cooper C, Dequeker J, Eastell R, Felsch B, Gowin W, Havelka S, Hoszowski K, Jajic I, Janott J, Johnell O, Kanis JA, Kragl G, Lopes Vaz A, Lorenc R, Lyritis G, Masaryk P, Matthis C, Miazgowski T, Parisi G, Pols HA, Poor G, Raspe HH, Reid DM, Reisinger W, Schedit-Nave C, Stepan JJ, Todd CJ, Weber K, Woolf AD, Yershova OB, Reeve J, O'Neill TW. Incidence of vertebral fracture in europe:results from the European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS) J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:716–724. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
