Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38826036
- PMCID: PMC11145993
- DOI: 10.1177/2515690X241258403
Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: A systematic review and meta-analysis have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of alkalinization for COVID-19 patients based on current evidence to determine the impact of alkalinization on COVID-19 outcomes.
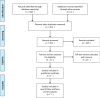
Methods: We searched MEDLINE (Pubmed), Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinicaltrials.gov for studies evaluating the efficacy of alkalinization up to 30 April 2023. Based on the PRISMA 2020 statement criteria a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies were performed.
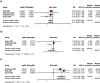
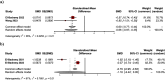
Results: The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in mortality rate in the alkalinization group compared to controls (RR 0.73, 95% CI: 0.56-0.95; I2 = 0%). However, our subgroup analysis showed no significant improvement in RCT-only studies (RR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.59-1.05; I2 = 0%), the recovery rate was significantly higher in the alkalinization group (RR 2.13, 95% CI: 1.39-3.26; I2 = 0%), duration of recovery also has improved in alkalinization group (SMD 0.76, 95% CI: 0.33-1.18; I2 = 0%). The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in the duration of hospitalization in the alkalinization group compared to controls with very low certainty of evidence (SMD -0.66, 95% CI: -0.97 to -0.35; I2 = 36%).
Conclusion: With low certainty of evidence, alkalinization (by sodium bicarbonate) can be an efficient and safe adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 patients. Future randomized controlled trials are needed to strengthen the available evidence.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; alkalinization; mortality; sodium bicarbonate; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declare that they have no known competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interventions for treatment of COVID-19: A living systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (The LIVING Project).PLoS Med. 2020 Sep 17;17(9):e1003293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003293. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32941437 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients.Virol J. 2022 Jun 13;19(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35698151 Free PMC article.
-
Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 20;5(5):CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 1;2:CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub5. PMID: 34013969 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis from randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0300512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300512. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753761 Free PMC article.
-
Fluvoxamine in Nonhospitalized Patients With Acute COVID-19 Infection and the Lack of Efficacy in Reducing Rates of Hospitalization, Mechanical Ventilation, and Mortality in Placebo-Controlled Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Ther. 2022 May-Jun 01;29(3):e298-e304. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000001496. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Am J Ther. 2022. PMID: 35383578
Cited by
-
The effects of urine alkalinization on kidney function in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a proof-of-concept randomized clinical trial.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025 Mar 7;13(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40635-025-00739-7. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2025. PMID: 40055234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheema HA, Rehman AU, Elrashedy AA, et al. Antiandrogens for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Med Virol. 2023;95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous