Hyperactivation of MEK1 in cortical glutamatergic neurons results in projection axon deficits and aberrant motor learning
- PMID: 38826084
- PMCID: PMC11247507
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.050570
Hyperactivation of MEK1 in cortical glutamatergic neurons results in projection axon deficits and aberrant motor learning
Abstract
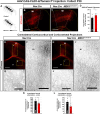
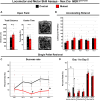
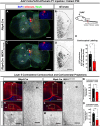
Abnormal extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2, encoded by Mapk3 and Mapk1, respectively) signaling is linked to multiple neurodevelopmental diseases, especially the RASopathies, which typically exhibit ERK1/2 hyperactivation in neurons and non-neuronal cells. To better understand how excitatory neuron-autonomous ERK1/2 activity regulates forebrain development, we conditionally expressed a hyperactive MEK1 (MAP2K1) mutant, MEK1S217/221E, in cortical excitatory neurons of mice. MEK1S217/221E expression led to persistent hyperactivation of ERK1/2 in cortical axons, but not in soma/nuclei. We noted reduced axonal arborization in multiple target domains in mutant mice and reduced the levels of the activity-dependent protein ARC. These changes did not lead to deficits in voluntary locomotion or accelerating rotarod performance. However, skilled motor learning in a single-pellet retrieval task was significantly diminished in these MEK1S217/221E mutants. Restriction of MEK1S217/221E expression to layer V cortical neurons recapitulated axonal outgrowth deficits but did not affect motor learning. These results suggest that cortical excitatory neuron-autonomous hyperactivation of MEK1 is sufficient to drive deficits in axon outgrowth, which coincide with reduced ARC expression, and deficits in skilled motor learning. Our data indicate that neuron-autonomous decreases in long-range axonal outgrowth may be a key aspect of neuropathogenesis in RASopathies.
Keywords: Axon; Connectivity; Cortex; Development; Kinase; RASopathy.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Altmüller, F., Pothula, S., Annamneedi, A., Nakhaei-Rad, S., Montenegro-Venegas, C., Pina-Fernández, E., Marini, C., Santos, M., Schanze, D., Montag, D.et al. (2017). Aberrant neuronal activity-induced signaling and gene expression in a mouse model of RASopathy. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006684. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006684 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andelfinger, G., Marquis, C., Raboisson, M.-J., Théoret, Y., Waldmüller, S., Wiegand, G., Gelb, B. D., Zenker, M., Delrue, M.-A. and Hofbeck, M. (2019). Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in noonan syndrome treated by MEK-inhibition. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 73, 2237-2239. 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angara, K., Pai, E. L.-L., Bilinovich, S. M., Stafford, A. M., Nguyen, J. T., Li, K. X., Paul, A., Rubenstein, J. L. and Vogt, D. (2020). Nf1 deletion results in depletion of the Lhx6 transcription factor and a specific loss of parvalbumin + cortical interneurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 117, 6189-6195. 10.1073/pnas.1915458117 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

