Energy and nutrient intake by 11-13-year-old young adolescents attending private schools in Delhi, India
- PMID: 38826089
- PMCID: PMC11473200
- DOI: 10.1017/S000711452400120X
Energy and nutrient intake by 11-13-year-old young adolescents attending private schools in Delhi, India
Abstract
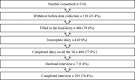
There are no high-quality data on dietary behaviour of adolescents in India. This study aimed to assess the intake of energy (E), macronutrients and selected micronutrients in a sample of 11-13-year-old schoolchildren in Delhi, India. Participants from private schools (n=10) recorded dietary intake using a 3-d food diary. Information was entered into the dietary assessment tool, Intake24, to ascertain portion size and convert data into nutrient intake through integrated food tables. Of the 514 consenting participants, 393 (76·4 %) (169 girls, 224 boys) aged 11·4 (±1·8) years completed the study. The median (interquartile range (IQR) daily E intake was 2580 (2139·3-2989·8) kcal (10·8 (9·0 - 12·5) MJ) for girls and 2941·5 (2466·7-3599·3) kcal (12·3 (10·3-15·2) MJ) for boys. The median (IQR) daily nutrient intakes for girls and boys respectively were protein 64·6 (54·8-79·3) g, 74·4 (61·4; 89·4) g; carbohydrate 336·5 (285·3-393·6) g, 379·6 (317·8-461·8) g; and saturated fat 45·6 (34·8-58·3) g, 54·6 (41·9-69·5) g. There were no significant between-gender differences in percentage E from protein (10·2 (9·2-11·4)), or carbohydrate (52·4 (48·7-56·7)). Girls obtained less percentage E from saturated fat (16·1 (11·0-18·2) compared with boys 16·3 (14·2-19·1) (P < 0·05). E from saturated fat was above FAO recommendations in >74 % of participants. The estimated average requirement for iron was achieved by < 40 % of girls. In conclusion, strategies to optimise the dietary intake of adolescents in India should focus on preventing excess intakes of E and saturated fat and improving iron intake in girls.
Keywords: Dietary fats; Dietary reference intakes; Eating: Nutrients; Nutrition status.
© The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Nutrition Society
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 10;(6):CD011737. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011737. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 19;5:CD011737. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011737.pub2. PMID: 26068959 Updated.
-
Dietary Intake of Competitive Bodybuilders.Sports Med. 2015 Jul;45(7):1041-63. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0329-4. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25926019
-
Adaptive e-learning to improve dietary behaviour: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Oct;15(37):1-160. doi: 10.3310/hta15370. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 22030014 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison between food frequency questionnaire and 24-hour dietary recall or weighing methods in evaluating dietary nutrient intakes of pregnant women].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2025 May;54(3):455-464. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2025.03.016. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40550613 Chinese.
-
Anthropometry, dietary intake, physical activity and sitting time patterns in adolescents aged 15-17 years: an international comparison in eight Latin American countries.BMC Pediatr. 2020 Jan 21;20(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-1920-x. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 31964386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNICEF (2023) Adolescent Development and Participation. New York: UNICEF.
-
- Kupka R, Siekmans K & Beal T (2020) The diets of children: overview of available data for children and adolescents. Global Food Secur 27, 100442.
-
- Sullivan CJ, Childs KK & O’Connell D (2010) Adolescent risk behavior subgroups: an empirical assessment. J Youth Adolescence 39, 541–562. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India, UNICEF & Population Council (2019) Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey (CNNS) National Report. New Delhi: MoHFW, UNICEF.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources