This is a preprint.
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 38826197
- PMCID: PMC11142227
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.24.595774
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway
Update in
-
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2403133121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403133121. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39141346 Free PMC article.
Abstract
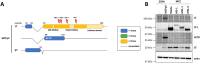
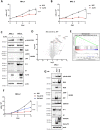
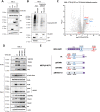
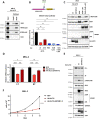
Polyomaviruses are small, circular dsDNA viruses that can cause cancer. Alternative splicing of polyomavirus early transcripts generates large and small tumor antigens (LT, ST) that play essential roles in viral replication and tumorigenesis. Some polyomaviruses also express middle tumor antigens (MTs) or Alternate LT ORFs (ALTOs), which are evolutionarily related but have distinct gene structures. MTs are a splice variant of the early transcript whereas ALTOs are overprinted on the second exon of the LT transcript in an alternate reading frame and are translated via an alternative start codon. Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV), the only human polyomavirus that causes cancer, encodes an ALTO but its role in the viral lifecycle and tumorigenesis has remained elusive. Here, we show MCPyV ALTO acts as a tumor suppressor and is silenced in Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC). Rescuing ALTO in MCC cells induces growth arrest and activates NF-κB signaling. ALTO activates NF-κB by binding SQSTM1 and TRAF2&3 via two N-Terminal Activating Regions (NTAR1+2), resembling Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).. Following activation, NF-κB dimers bind the MCPyV non-coding control region (NCCR) and downregulate early transcription. Beyond MCPyV, NTAR motifs are conserved in other polyomavirus ALTOs, which activate NF-κB signaling, but are lacking in MTs that do not. Furthermore, polyomavirus ALTOs downregulate their respective viral early transcription in an NF-κB and NTAR dependent manner. Our findings suggest that ALTOs evolved to suppress viral replication and promote viral latency and that MCPyV ALTO must be silenced for MCC to develop.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Merkel cell carcinoma; NF-κB; alternate LT open reading frame (ALTO); polyomavirus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polyomavirus ALTOs, but not MTs, downregulate viral early gene expression by activating the NF-κB pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2403133121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2403133121. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39141346 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin-Specific Protease Usp7, a Novel Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T-Antigen Interaction Partner, Modulates Viral DNA Replication.J Virol. 2020 Feb 14;94(5):e01638-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01638-19. Print 2020 Feb 14. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31801860 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Activates Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling to Promote Tumorigenesis.Mol Cancer Res. 2020 Nov;18(11):1623-1637. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0587. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Mol Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32753470 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus and non-Merkel cell carcinomas: guilty or circumstantial evidence?APMIS. 2020 Feb;128(2):104-120. doi: 10.1111/apm.13019. Epub 2020 Jan 28. APMIS. 2020. PMID: 31990105 Review.
-
The Human Polyomavirus Middle and Alternative T-Antigens; Thoughts on Roles and Relevance to Cancer.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 8;9:398. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00398. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29568287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V., T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature 278, 261–263 (1979). - PubMed
-
- DeCaprio J. A. et al., SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell 54, 275–283 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E., Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature 303, 435–439 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M., Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature 315, 239–242 (1985). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
