This is a preprint.
TGF-β Signaling in Cranial Neural Crest Affects Late-Stage Mandibular Bone Resorption and Length
- PMID: 38826301
- PMCID: PMC11142237
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.24.595783
TGF-β Signaling in Cranial Neural Crest Affects Late-Stage Mandibular Bone Resorption and Length
Update in
-
TGF-β signaling in the cranial neural crest affects late-stage mandibular bone resorption and length.Front Physiol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1435594. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1435594. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39473613 Free PMC article.
Abstract
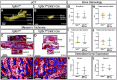
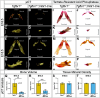
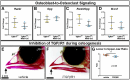
Malocclusions are common craniofacial malformations which cause quality of life and health problems if left untreated. Unfortunately, the current treatment for severe skeletal malocclusion is invasive surgery. Developing improved therapeutic options requires a deeper understanding of the cellular mechanisms responsible for determining jaw bone length. We have recently shown that neural crest mesenchyme (NCM) can alter jaw length by controlling recruitment and function of mesoderm-derived osteoclasts. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling is critical to craniofacial development by directing bone resorption and formation, and heterozygous mutations in TGF-β type I receptor (TGFBR1) are associated with micrognathia in humans. To identify what role TGF-β signaling in NCM plays in controlling osteoclasts during mandibular development, mandibles of mouse embryos deficient in the gene encoding Tgfbr1 specifically in NCM were analyzed. Our lab and others have demonstrated that Tgfbr1fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mice display significantly shorter mandibles with no condylar, coronoid, or angular processes. We hypothesize that TGF-β signaling in NCM can also direct later bone remodeling and further regulate late embryonic jaw bone length. Interestingly, analysis of mandibular bone through micro-computed tomography and Masson's trichrome revealed no significant difference in bone quality between the Tgfbr1fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mice and controls, as measured by bone perimeter/bone area, trabecular rod-like diameter, number and separation, and gene expression of Collagen type 1 alpha 1 (Col1α1) and Matrix metalloproteinase 13 (Mmp13). Though there was not a difference in localization of bone resorption within the mandible indicated by TRAP staining, Tgfbr1fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mice had approximately three-fold less osteoclast number and perimeter than controls. Gene expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-β (Rank) and Mmp9, markers of osteoclasts and their activity, also showed a three-fold decrease in Tgfbr1fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mandibles. Evaluation of osteoblast-to-osteoclast signaling revealed no significant difference between Tgfbr1fl/fl;Wnt1-Cre mandibles and controls, leaving the specific mechanism unresolved. Finally, pharmacological inhibition of Tgfbr1 signaling during the initiation of bone mineralization and resorption significantly shortened jaw length in embryos. We conclude that TGF-β signaling in NCM decreases mesoderm-derived osteoclast number, that TGF-β signaling in NCM impacts jaw length late in development, and that this osteoblast-to-osteoclast communication may be occurring through an undescribed mechanism.
Keywords: Transforming Growth Factor-beta Type I Receptor; bone remodeling; bone resorption; jaw; mandible; maxillofacial development; neural crest; osteoclasts.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGF-β signaling in the cranial neural crest affects late-stage mandibular bone resorption and length.Front Physiol. 2024 Oct 15;15:1435594. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1435594. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39473613 Free PMC article.
-
Neural crest-mediated bone resorption is a determinant of species-specific jaw length.Dev Biol. 2015 Dec 1;408(1):151-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26449912 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta mediated Dlx5 signaling plays a crucial role in osteo-chondroprogenitor cell lineage determination during mandible development.Dev Biol. 2008 Sep 15;321(2):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.03.046. Epub 2008 Apr 15. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18684439 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Jaw Length During Development, Disease, and Evolution.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;115:271-98. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26589929 Review.
-
The Role Of BMPs in the Regulation of Osteoclasts Resorption and Bone Remodeling: From Experimental Models to Clinical Applications.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;13:869422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869422. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35558080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albanese CT, Harrison MR. Surgical treatment for fetal disease. The state of the art. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998;847:74–85. - PubMed
-
- Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM, Levin LS. Syndromes of the Head and Neck: Oxford University Press; 1990.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
