This is a preprint.
Loss of a conserved C-terminal region of the Aspergillus fumigatus AtrR transcriptional regulator leads to a gene-specific defect in target gene expression
- PMID: 38826412
- PMCID: PMC11142210
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.22.595332
Loss of a conserved C-terminal region of the Aspergillus fumigatus AtrR transcriptional regulator leads to a gene-specific defect in target gene expression
Abstract
Treatment of fungal infections associated with the filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus is becoming more problematic as this organism is developing resistance to the main chemotherapeutic drug at an increasing rate. Azole drugs represent the current standard-of-care in treatment of aspergillosis with this drug class acting by inhibiting a key step in biosynthesis of the fungal sterol ergosterol. Azole compounds block the activity of the lanosterol α-14 demethylase, encoded by the cyp51A gene. A common route of azole resistance involves an increase in transcription of cyp51A. This transcriptional increase requires the function of a Zn2Cys6 DNA-binding domain-containing transcription activator protein called AtrR. AtrR was identified through its action as a positive regulator of expression of an ATP-binding cassette transporter (abcC/cdr1B here called abcG1). Using both deletion and alanine scanning mutagenesis, we demonstrate that a conserved C-terminal domain in A. fumigatus is required for expression of abcG1 but dispensable for cyp51A transcription. This domain is also found in several other fungal pathogen AtrR homologues consistent with a conserved gene-selective function of this protein segment being conserved. Using RNA-seq, we find that this gene-specific transcriptional defect extends to several other membrane transporter-encoding genes including a second ABC transporter locus. Our data reveal that AtrR uses at least two distinct mechanisms to induce gene expression and that normal susceptibility to azole drugs cannot be provided by maintenance of wild-type expression of the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway when ABC transporter expression is reduced.
Figures
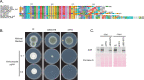
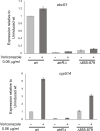
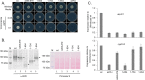


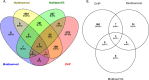

References
-
- Verweij PE, Snelders E, Kema GH, Mellado E, Melchers WJ. 2009. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: a side-effect of environmental fungicide use? Lancet Infect Dis 9:789–95. - PubMed
-
- Snelders E, Melchers WJ, Verweij PE. 2011. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: a new challenge in the management of invasive aspergillosis? Future Microbiol 6:335–47. - PubMed
-
- Rhodes J, Abdolrasouli A, Dunne K, Sewell TR, Zhang Y, Ballard E, Brackin AP, van Rhijn N, Chown H, Tsitsopoulou A, Posso RB, Chotirmall SH, McElvaney NG, Murphy PG, Talento AF, Renwick J, Dyer PS, Szekely A, Bowyer P, Bromley MJ, Johnson EM, Lewis White P, Warris A, Barton RC, Schelenz S, Rogers TR, Armstrong-James D, Fisher MC. 2022. Population genomics confirms acquisition of drug-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus infection by humans from the environment. Nat Microbiol 7:663–674. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
