This is a preprint.
Co-dependent formation of the Toxoplasma gondii sub-pellicular microtubules and inner membrane skeleton
- PMID: 38826480
- PMCID: PMC11142238
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.25.595886
Co-dependent formation of the Toxoplasma gondii sub-pellicular microtubules and inner membrane skeleton
Update in
-
Co-dependent formation of the Toxoplasma gondii subpellicular microtubules and inner membrane skeleton.mBio. 2025 Sep 10;16(9):e0138925. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01389-25. Epub 2025 Aug 13. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40801525 Free PMC article.
Abstract
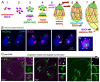
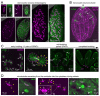
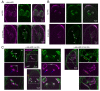
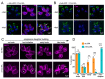
One of the defining features of apicomplexan parasites is their cytoskeleton composed of alveolar vesicles, known as the inner membrane complex (IMC) undergirded by intermediate-like filament network and an array of subpellicular microtubules (SPMTs). In Toxoplasma gondii, this specialized cytoskeleton is involved in all aspects of the disease-causing lytic cycle, and notably acting as a scaffold for parasite offspring in the internal budding process. Despite advances in our understanding of the architecture and molecular composition, insights pertaining to the coordinated assembly of the scaffold are still largely elusive. Here, T. gondii tachyzoites were dissected by advanced, iterative expansion microscopy (pan-ExM) revealing new insights into the very early sequential formation steps of the tubulin scaffold. A comparative study of the related parasite Sarcocystis neurona revealed that different MT bundling organizations of the nascent SPMTs correlate with the number of central and basal alveolar vesicles. In absence of a so far identified MT nucleation mechanism, we genetically dissected T. gondii γ-tubulin and γ-tubulin complex protein 4 (GCP4). While γ-tubulin depletion abolished the formation of the tubulin scaffold, a set of MTs still formed that suggests SPMTs are nucleated at the outer core of the centrosome. Depletion of GCP4 interfered with the correct assembly of SPMTs into the forming daughter buds, further indicating that the parasite utilizes the γ-tubulin complex in tubulin scaffold formation .
Keywords: APR; IMC; SFA; Sarcocystis; Toxoplasma; alveoli; microtubules; γ-tubulin; γTuRC.
Figures



References
-
- Gubbels M.J., Keroack C.D., Dangoudoubiyam S., Worliczek H.L., Paul A.S., Bauwens C., Elsworth B., Engelberg K., Howe D.K., Coppens I., and Duraisingh M.T., 2020. Fussing About Fission: Defining Variety Among Mainstream and Exotic Apicomplexan Cell Division Modes. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 10: 269. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harding C.R. and Frischknecht F., 2020. The Riveting Cellular Structures of Apicomplexan Parasites. Trends Parasitol, 36: 979–991. - PubMed
-
- Gubbels M.J. and Morrissette N.S., The Toxoplasma cytoskeleton: structures, proteins, and processes, in Toxoplasma gondii: the model apicomplexan - perspective and methods, Weiss L.M. and Kim K., Editors. 2020, Academic Press: London, IK. 743–788.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
