Visualization and Analysis of Mapping Knowledge Domain of Fluid Flow Related to Microfluidic Chip
- PMID: 38826539
- PMCID: PMC11137721
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00966
Visualization and Analysis of Mapping Knowledge Domain of Fluid Flow Related to Microfluidic Chip
Abstract
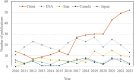
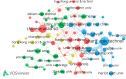
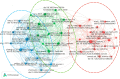
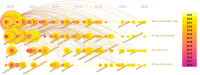
Microfluidic chips are important tools to study the microscopic flow of fluid. To better understand the research clues and development trends related to microfluidic chips, a bibliometric analysis of microfluidic chips was conducted based on 1115 paper records retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database. CiteSpace and VOSviewer software were used to analyze the distribution of annual paper quantity, country/region distribution, subject distribution, institution distribution, major source journals distribution, highly cited papers, coauthor cooperation relationship, research knowledge domain, research focuses, and research frontiers, and a knowledge domain map was drawn. The results show that the number of papers published on microfluidic chips increased from 2010 to 2023, among which China, the United States, Iran, Canada, and Japan were the most active countries in this field. The United States was the most influential country. Nanoscience, energy, and chemical industry and multidisciplinary materials science were the main fields of microfluidic chip research. Lab on a Chip, Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, and Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering were the main sources of papers published. The fabrication of chips, as well as their applications in porous media flow and multiphase flow, is the main knowledge domain of microfluidic chips. Micromodeling, fluid displacement, wettability, and multiphase flow are the research focuses in this field currently. The research frontiers in this field are enhanced oil recovery, interfacial tension, and stability.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Bibliometric study of plastics microfluidic chip from 1994 to 2022: A review.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 20;11(2):e42102. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42102. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39906818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Applications of microfluidic paper-based chips in environmental analysis and detection].Se Pu. 2021 Aug;39(8):802-815. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.09004. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34212581 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Visualization analysis on treatment of coronavirus based on knowledge graph].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Mar;32(3):279-286. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200225-00200. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32385990 Chinese.
-
Knowledge domain, research hotspots and frontiers in physiology teaching reforms from 2012 to 2021: A bibliometric and knowledge-map analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 20;10:1031713. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1031713. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37020677 Free PMC article.
-
Multiphase displacement manipulated by micro/nanoparticle suspensions in porous media via microfluidic experiments: From interface science to multiphase flow patterns.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023 Jan;311:102826. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102826. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2023. PMID: 36528919 Review.
References
-
- Cui Y. T., Wang Z., Sun C., Sheng Y., Yu C., Zhou C.. et al.The Measurement of Flow Rate of Micro-fluid On-chip by Digital Holography: HOLOGRAPHY, DIFFRACTIVE, OPTICS, AND APPLICATIONS VII[Z]. Conference on Holography, Diffractive Optics, and Applications VII: 2017: 10022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
