Artificial intelligence based glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy detection using MATLAB - retrained AlexNet convolutional neural network
- PMID: 38826575
- PMCID: PMC11143403
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.122288.2
Artificial intelligence based glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy detection using MATLAB - retrained AlexNet convolutional neural network
Abstract
Background: Glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy (DR) are the leading causes of irreversible retinal damage leading to blindness. Early detection of these diseases through regular screening is especially important to prevent progression. Retinal fundus imaging serves as the principal method for diagnosing glaucoma and DR. Consequently, automated detection of eye diseases represents a significant application of retinal image analysis. Compared with classical diagnostic techniques, image classification by convolutional neural networks (CNN) exhibits potential for effective eye disease detection.
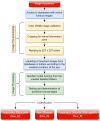
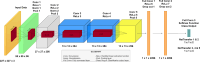
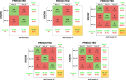
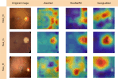
Methods: This paper proposes the use of MATLAB - retrained AlexNet CNN for computerized eye diseases identification, particularly glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, by employing retinal fundus images. The acquisition of the database was carried out through free access databases and access upon request. A transfer learning technique was employed to retrain the AlexNet CNN for non-disease (Non_D), glaucoma (Sus_G) and diabetic retinopathy (Sus_R) classification. Moreover, model benchmarking was conducted using ResNet50 and GoogLeNet architectures. A Grad-CAM analysis is also incorporated for each eye condition examined.
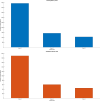
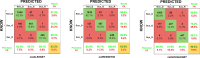
Results: Metrics for validation accuracy, false positives, false negatives, precision, and recall were reported. Validation accuracies for the NetTransfer (I-V) and netAlexNet ranged from 89.7% to 94.3%, demonstrating varied effectiveness in identifying Non_D, Sus_G, and Sus_R categories, with netAlexNet achieving a 93.2% accuracy in the benchmarking of models against netResNet50 at 93.8% and netGoogLeNet at 90.4%.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the efficacy of using a MATLAB-retrained AlexNet CNN for detecting glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. It emphasizes the need for automated early detection tools, proposing CNNs as accessible solutions without replacing existing technologies.
Keywords: AlexNet; Classification; Convolutional Neural Network (CNN); Diabetic Retinopathy; Glaucoma.
Copyright: © 2024 Arias-Serrano I et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ResViT FusionNet Model: An explainable AI-driven approach for automated grading of diabetic retinopathy in retinal images.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Mar;186:109656. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109656. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39823821
-
Advancing glaucoma detection with convolutional neural networks: a paradigm shift in ophthalmology.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul-Sep;67(3):222-237. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2023.39. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37876506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Artificial Intelligence Driven Approach for Classification of Ophthalmic Images using Convolutional Neural Network: An Experimental Study.Curr Med Imaging. 2024;20:e15734056286918. doi: 10.2174/0115734056286918240419100058. Curr Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38721793
-
Transfer Learning for Automated OCTA Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020 Jul 2;9(2):35. doi: 10.1167/tvst.9.2.35. eCollection 2020 Jul. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32855839 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic retinopathy screening through artificial intelligence algorithms: A systematic review.Surv Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep-Oct;69(5):707-721. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2024.05.008. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Surv Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38885761
Cited by
-
Classification of Monkeypox Images Using LIME-Enabled Investigation of Deep Convolutional Neural Network.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 5;13(9):1639. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091639. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37175030 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Model Based on You Only Look Once Algorithm for Detection and Visualization of Fracture Areas in Three-Dimensional Skeletal Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 20;14(1):11. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14010011. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qummar S, Khan FG, Shah S, et al. : A Deep Learning Ensemble Approach for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection. IEEE Access. 2019;7:150530–150539. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). 10.1109/access.2019.2947484 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

