Neuroprotective effects of dantrolene in neurodegenerative disease: Role of inhibition of pathological inflammation
- PMID: 38826587
- PMCID: PMC11138240
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jatmed.2024.04.002
Neuroprotective effects of dantrolene in neurodegenerative disease: Role of inhibition of pathological inflammation
Abstract
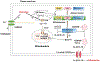
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) refer to a group of diseases in which slow, continuous cell death is the main pathogenic event in the nervous system. Most NDs are characterized by cognitive dysfunction or progressive motor dysfunction. Treatments of NDs mainly target alleviating symptoms, and most NDs do not have disease-modifying drugs. The pathogenesis of NDs involves inflammation and apoptosis mediated by mitochondrial dysfunction. Dantrolene, approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, acts as a RyRs antagonist for the treatment of malignant hyperthermia, spasticity, neuroleptic syndrome, ecstasy intoxication and exertional heat stroke with tolerable side effects. Recently, dantrolene has also shown therapeutic effects in some NDs. Its neuroprotective mechanisms include the reduction of excitotoxicity, apoptosis and neuroinflammation. In summary, dantrolene can be considered as a potential therapeutic candidate for NDs.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Apoptosis; Calcium; Cognitive dysfunction; Progressive motor dysfunction; Pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Henry Liu holds the position of Editor-in-Chief for JATM, and was blinded from reviewing or making decisions for the manuscript. Dr. Huafeng Wei is one of the inventors for patents application titled “Intranasal dantrolene for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease” owned by the University of Pennsylvania Trustee in following countries: International (PCTUS2020/040198, 2020), USA (62/868,820, 2019), Europe (20833145.4–1112, 2022), Japan (2021-577376, 2021), China (202080054348.2, 2022), Hong Kong (62022053033.60, 2020), South Korea (10-2022-7003375, 2020), Singapore (11202114347V, 2020), Brazil (BR1120210265970, 2020), Mexico (MX/a/2022/000231, 2022). The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of traditional Chinese medicine in ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction via non-coding RNA signaling: Implication in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;14:1123188. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1123188. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dantrolene. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in malignant hyperthermia, the neuroleptic malignant syndrome and an update of its use in muscle spasticity.Drugs. 1986 Aug;32(2):130-68. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198632020-00003. Drugs. 1986. PMID: 3527659 Review.
-
To re-examine the intersection of microglial activation and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases from the perspective of pyroptosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 9;15:1284214. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1284214. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38020781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets Underlying the Neuroprotective Effects of Boswellic Acid: A Systematic Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(19):1912-1925. doi: 10.2174/1389557523666230330113611. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36998129
-
Effects of Naodesheng tablets on amyloid beta-induced dysfunction: A traditional Chinese herbal formula with novel therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease revealed by systems pharmacology.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111916. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111916. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34328103
Cited by
-
Dantrolene Protects Hippocampal Neurons Against Amyloid-β₁₋₄₂-Induced Calcium Dysregulation and Cell Death.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 12;50(3):198. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04460-5. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40504441
-
Intranasal Delivery of Lithium Salt Suppresses Inflammatory Pyroptosis in the brain and Ameliorates Memory Loss and Depression-like Behavior in 5XFAD mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 12:2024.09.18.613794. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.18.613794. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17;20(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10185-7. PMID: 39345574 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Intranasal Delivery of Lithium Salt Suppresses Inflammatory Pyroptosis in the Brain and Ameliorates Memory Loss and Depression-like Behavior in 5XFAD Mice.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17;20(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s11481-025-10185-7. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40095208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Masi A, Narducci R, Mannaioni G. Harnessing ionic mechanisms to achieve disease modification in neurodegenerative disorders. Pharmacol Res. 2019;147:104343. - PubMed
-
- 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement; 19(4); 2023: p. 1598–695. - PubMed
-
- Hou Y, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(10):565–581. - PubMed
-
- Bates GP, et al. Huntington disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2015;1:15005. - PubMed
-
- Brown CA, et al. Estimated prevalence and incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and SOD1 and C9orf72 genetic variants. Neuroepidemiology. 2021;55(5):342–353. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
