Parasitic infections: A new frontier for PGD2 functions
- PMID: 38826690
- PMCID: PMC11140190
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2024.100078
Parasitic infections: A new frontier for PGD2 functions
Abstract
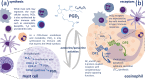
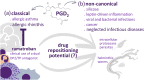
Prostaglandin (PG)D2 is produced and/or triggered by different parasites to modulate the course of the infection. These findings position PGD2 as a therapeutic target and suggest potential beneficial effects of repositioned drugs that target its synthesis or receptor engagement. However, recent in vivo data may suggest a more nuanced role and warrants further investigation of the role of PGD2 during the full course and complexity of parasitic infections.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Bruno L. Diaz reports financial support was provided by Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Research Support of Rio de Janeiro State. Christianne Bandeira-Melo reports financial support was provided by Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Research Support of Rio de Janeiro State. Christianne Bandeira-Melo reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100003593National Council for Scientific and Technological Development. Bruno L. Diaz reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100003593National Council for Scientific and Technological Development. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inactivation of CES1 Blocks Prostaglandin D2 Glyceryl Ester Catabolism in Monocytes/Macrophages and Enhances Its Anti-inflammatory Effects, Whereas the Pro-inflammatory Effects of Prostaglandin E2 Glyceryl Ester Are Attenuated.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 3;5(45):29177-29188. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03961. eCollection 2020 Nov 17. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33225149 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of the prostaglandin D2/prostaglandin DP1 receptor and lipocalin-type prostaglandin D2 synthase/prostaglandin D2 pathways in bacteria-induced bovine endometrial tissue.Vet Res. 2022 Nov 26;53(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01100-6. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36435808 Free PMC article.
-
The endogenous bioactive lipid prostaglandin D2-glycerol ester reduces murine colitis via DP1 and PPARγ receptors.FASEB J. 2018 Sep;32(9):5000-5011. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701205R. Epub 2018 Apr 9. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29630407
-
Discovery of anti-inflammatory role of prostaglandin D2.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Dec 1;78(11):1643-1647. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0347. Epub 2016 Aug 5. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27498997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in PGD2/PTGDR2 signaling pathway in tumors: A review.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Sep 6;24(5):1055-1067. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10485. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38704736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous PGD2 acting on DP2 receptor counter regulates Schistosoma mansoni infection-driven hepatic granulomatous fibrosis.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 22;20(8):e1011812. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011812. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39173086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alafiatayo R.A., Cookson M.R., Pentreath V.W. Production of prostaglandins D2 and E2 by mouse fibroblasts and astrocytes in culture caused byTrypanosoma brucei brucei products and endotoxin. Parasitol. Res. 1994;80(3):223–229. - PubMed
-
- Bundy G.L. Nonmammalian sources of eicosanoids. Advances in prostaglandin, thromboxane, and leukotriene research. 1985;14:229–262. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

