Comparison of Three Deep Learning Models in Accurate Classification of 770 Dermoscopy Skin Lesion Images
- PMID: 38827104
- PMCID: PMC11141796
Comparison of Three Deep Learning Models in Accurate Classification of 770 Dermoscopy Skin Lesion Images
Abstract
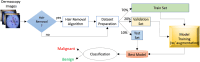
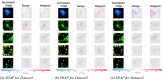
Accurately determining and classifying different types of skin cancers is critical for early diagnosis. In this work, we propose a novel use of deep learning for classification of benign and malignant skin lesions using dermoscopy images. We obtained 770 de-identified dermoscopy images from the University of Missouri (MU) Healthcare. We created three unique image datasets that contained the original images and images obtained after applying a hair removal algorithm. We trained three popular deep learning models, namely, ResNet50, DenseNet121, and Inception-V3. We evaluated the accuracy and the area under the curve (AUC) receiver operating characteristic (ROC) for each model and dataset. DenseNet121 achieved the best accuracy (80.52%) and AUC ROC score (0.81) on the third dataset. For this dataset, the sensitivity and specificity were 0.80 and 0.81, respectively. We also present the SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) values for the predictions made by different models to understand their interpretability.
©2024 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improving Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Ultrasound Images Using Deep Learning with Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanism.Acad Radiol. 2025 May 27:S1076-6332(25)00435-0. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.05.007. Online ahead of print. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40436710
-
Integrated convolutional neural network for skin cancer classification with hair and noise restoration.Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Oct 16;55(1):161-177. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5954. eCollection 2025. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 40104314 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Approaches for the Classification of Keloid Images in the Context of Malignant and Benign Skin Disorders.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 12;15(6):710. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060710. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150053 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Approaches Towards Skin Lesion Segmentation and Classification from Dermoscopic Images - A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(5):513-533. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666190129120449. Curr Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32484086 Review.
-
Multi-features extraction based on deep learning for skin lesion classification.Tissue Cell. 2022 Feb;74:101701. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2021.101701. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 34861582 Review.
References
-
- Incidence and clinical characteristics of nonmelanoma skin cancers among Hispanic and Asian patients in the US: A 5-year, single institution retrospective review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May 1;72(5, Supplement 1):AB186. - PubMed
-
- Chen JG, Fleischer Jr AB, Smith ED, Kancler C, Goldman ND, Williford PM, et al. Cost of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer Treatment in the United States. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27(12):1035–8. - PubMed
-
- Ko JM, Velez NF, Tsao H. Pathways to melanoma. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010 Dec;29(4):210–7. - PubMed
-
- Cedars-Sinai. https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/articles.html .
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
