Nomogram for Predicting Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Treated with Insulin Pump During Enteral Nutrition
- PMID: 38827166
- PMCID: PMC11141570
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S436390
Nomogram for Predicting Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Treated with Insulin Pump During Enteral Nutrition
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a prediction model for hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients treated with an insulin pump during enteral nutrition.
Methods: This retrospective study included T2DM patients treated with an insulin pump during enteral nutrition at the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital, Foshan First People's Hospital, and Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine between January 2016 and December 2023. The patients were randomized 3:1 to the training and validation sets. The risk factors for hypoglycemia were analyzed. A prediction model was developed.
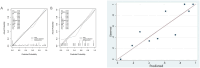
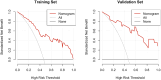
Results: This study included 122 patients, and 57 patients had at least one hypoglycemic event during their hospitalization (46.72%). The multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that the time to reach the glycemic targets (odds ratio (OR)=1.408, 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.084-1.825, P=0.006), average glycemia (OR=0.387, 95% CI=0.233-0.643, P=0.010), coronary heart disease (OR=0.089, 95% CI=0.016-0.497, P<0.001), and the administration of hormone therapy (OR=6.807, 95% CI=1.128-41.081, P=0.037) were independently associated with hypoglycemia. A nomogram was built. The receiver operating characteristics analysis showed that the area under the curve of the model was 0.872 (95% CI=0.0.803-0.940) for the training set and 0.839 (95% CI=0.688-0.991) in the validation set.
Conclusion: A nomogram was successfully built to predict hypoglycemia in T2DM patients treated with an insulin pump during enteral nutrition, based on the time to reach the glycemic targets, average glycemia, coronary heart disease, and the administration of hormone therapy.
Keywords: T2DM; enteral nutrition; hypoglycemia; insulin pump therapy; nomograms.
© 2024 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Park R, Hansell D, Davidson L, et al. Management of diabetic patients requiring nutritional support. Nutrition. 1992;8(5):316–320. - PubMed
-
- Eckert I, Kumbier MCC, Silva FM, Franzosi OS, de Almeida JC. Association of specialized enteral nutrition with glycemic control and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(6):3940–3949. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.030 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Ren S, Wang Y, Niu Z, Zhao H. Clinical study of enhancing the delivery of enteral nutrition in critically ill patients. Chin J Crit Care Med. 2018;38(2):145–148.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

