Aluminum chloride and D-galactose induced a zebrafish model of Alzheimer's disease with cognitive deficits and aging
- PMID: 38827230
- PMCID: PMC11140485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.05.036
Aluminum chloride and D-galactose induced a zebrafish model of Alzheimer's disease with cognitive deficits and aging
Abstract
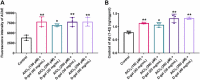
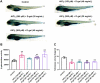
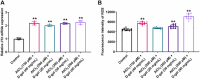
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder. Transgenic and pharmacological AD models are extensively studied to understand AD mechanisms and drug discovery. However, they are time-consuming and relatively costly, which hinders the discovery of potential anti-AD therapeutics. Here, we established a new model of AD in larval zebrafish by co-treatment with aluminum chloride (AlCl3) and D-galactose (D-gal) for 72 h. In particular, exposure to 150 μM AlCl3 + 40 mg/mL D-gal, 200 μM AlCl3 + 30 mg/mL D-gal, or 200 μM AlCl3 + 40 mg/mL D-gal successfully induced AD-like symptoms and aging features. Co-treatment with AlCl3 and D-gal caused significant learning and memory deficits, as well as impaired response ability and locomotor capacity in the plus-maze and light/dark test. Moreover, increased acetylcholinesterase and β-galactosidase activities, β-amyloid 1-42 deposition, reduced telomerase activity, elevated interleukin 1 beta mRNA expression, and enhanced reactive oxygen species production were also observed. In conclusion, our zebrafish model is simple, rapid, effective and affordable, incorporating key features of AD and aging, thus may become a unique and powerful tool for high-throughput screening of anti-AD compounds in vivo.
Keywords: Aluminum chloride; Alzheimer's disease; D-galactose; High-throughput screening; Zebrafish.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
d-galactose and aluminium chloride induced rat model with cognitive impairments.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:1602-1608. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.152. Epub 2018 May 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29864948
-
Protective effects of kinetin against aluminum chloride and D-galactose induced cognitive impairment and oxidative damage in mouse.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Sep;134:262-272. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28867383
-
Coconut oil ameliorates behavioral and biochemical alterations induced by D-GAL/AlCl3 in rats.Brain Res. 2024 Jan 15;1823:148704. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148704. Epub 2023 Dec 3. Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 38052316
-
Development of AD like symptoms following co-administration of AlCl3 and D-gal in rats: A neurochemical, biochemical and behavioural study.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017 Mar;30(2(Suppl.)):647-653. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28650335
-
The effects of valsartan on cognitive deficits induced by aluminum trichloride and d-galactose in mice.Neurol Res. 2014 Jul;36(7):651-8. doi: 10.1179/1743132813Y.0000000295. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Neurol Res. 2014. PMID: 24620968
Cited by
-
Lactylation and Central Nervous System Diseases.Brain Sci. 2025 Mar 11;15(3):294. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15030294. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40149815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From computational screening to zebrafish testing: repurposing of doxazosin, donepezil, and dolutegravir for neuroprotective potential in Alzheimer's disease.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10581-10595. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03933-2. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40014129
-
Salicylaldehyde Benzoylhydrazone Protects Against Ferroptosis in Models of Neurotoxicity and Behavioural Dysfunction, In Vitro and In Vivo.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Jun 14;75(2):77. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02371-2. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40515790 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Berberine Chloride Against the Aluminium Chloride-Induced Alzheimer's Disease in Zebra Fish Larvae.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 27. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01392-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40014257
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
