Quantitative assessment and correlational analysis of subjective and objective indicators in patients with allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 38827256
- PMCID: PMC11142756
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.0000000000000141
Quantitative assessment and correlational analysis of subjective and objective indicators in patients with allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: The diagnosis of allergic rhinitis is mainly based on the typical medical history, clinical manifestations, and corresponding allergen test results of the patients. However, there are often clinical inconsistencies among the 3.
Objective: To study the clinical characteristics of patients with allergic rhinitis from both subjective and objective aspects to determine the correlations between the quantitative assessment outcomes of subjective and objective indicators.
Methods: A total of 111 patients with allergic rhinitis who visited our outpatient clinic from June 2022 to December 2022 were selected. The 22-item sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT-22) and the visual analog scale (VAS) for the severity of the disease were used to score the subjective indicators of allergic rhinitis. The objective indicators of allergic rhinitis were evaluated by serum inhalant allergens immunoglobulin E test, nasal endoscopy modified Lund-Kennedy (MLK) scoring method, and acoustic rhinometry.
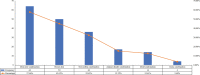
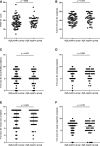
Results: SNOT-22 score, total VAS score for symptoms, and the VAS score for nasal itching were positively correlated with the number of positive allergens (r = 0.266, P = 0.005, r = 0.576, P < 0.001, and r = 0.271, P = 0.004, respectively). No differences were found in all subjective indicators scores between the total immunoglobulin E positive and negative groups (P > 0.05). SNOT-22 score, total VAS score for symptoms, and the VAS score for nasal congestion were positively correlated with MLK total score of nasal endoscopy (r = 0.343, P < 0.001, r = 0.438, P < 0.001, and r = 0.225, P = 0.018, respectively). Parameters of acoustic rhinometry were not correlated with the subjective indicators scores of allergic rhinitis (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: A multifaceted quantitative assessment of allergic rhinitis using a combination of subjective and objective methods can help physicians make an accurate diagnosis and create reasonable treatment plans.
Keywords: Acoustic rhinometry; allergens; allergic rhinitis; endoscopy; symptom assessment.
Copyright © 2024. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Effects of nasal polyps and allergy rhinitis on quantitative evaluation of subjective and objective assessment of chronic rhinosinusitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Jan 5;32(1):53-57. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.01.011. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29798211 Chinese.
-
The Evaluation Value of the Modified Lund-Kennedy Nasal Endoscopy Score on the Efficacy of Sublingual Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2024 Nov;38(6):366-372. doi: 10.1177/19458924241269786. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39152637
-
Correlations between IL-36 family cytokines in peripheral blood and subjective and objective assessment results in patients with allergic rhinitis.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2023 Aug 30;19(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13223-023-00834-y. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37649097 Free PMC article.
-
[Rhinitis in adults].Acta Med Croatica. 2011;65(2):181-7. Acta Med Croatica. 2011. PMID: 22359885 Review. Croatian.
-
A review of the efficacy of desloratadine, fexofenadine, and levocetirizine in the treatment of nasal congestion in patients with allergic rhinitis.Clin Ther. 2009 May;31(5):921-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.05.017. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19539095 Review.
References
-
- Bousquet J, Anto JM, Bachert C, Baiardini I, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Walter Canonica G, Melén E, Palomares O, Scadding GK, Togias A, Toppila-Salmi S. Allergic rhinitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:95. - PubMed
-
- Klimek L, Bergmann K, Biedermann T, Bousquet J, Hellings P, Jung K, Merk H, Olze H, Schlenter W, Stock P, Ring J, Wagenmann M, Wehrmann W, Mösges R, Pfaar O. Visual analogue scales (VAS): measuring instruments for the documentation of symptoms and therapy monitoring in cases of allergic rhinitis in everyday health care. Allergo J Int. 2017;26:16–24. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weinstein SF, Katial R, Jayawardena S, Pirozzi G, Staudinger H, Eckert L, Joish VN, Amin N, Maroni J, Rowe P, Graham NMH, Teper A. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in perennial allergic rhinitis and comorbid asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;142:171–177.e1. - PubMed
-
- Lauriello M, Di Rubbo V, Sinatti G, Pasqua M, Tucci C, di Marco G-P, Necozione S, Eibenstein A. Correlation between SNOT-22, nasal cytology, and mood disorders in patients with allergic rhinitis treated with a liposomal nasal spray. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2019;10:2152656719866809. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karli R, Balbaloglu E, Uzun L, Çinar F, Ugur MB. Correlation of symptoms with total IgE and specific IgE levels in patients presenting with allergic rhinitis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2013;7:75–79. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
