This is a preprint.
Surrogate modeling and control of medical digital twins
- PMID: 38827450
- PMCID: PMC11142319
Surrogate modeling and control of medical digital twins
Update in
-
Optimal control of agent-based models via surrogate modeling.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Jan 14;21(1):e1012138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012138. eCollection 2025 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 39808665 Free PMC article.
Abstract
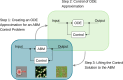
The vision of personalized medicine is to identify interventions that maintain or restore a person's health based on their individual biology. Medical digital twins, computational models that integrate a wide range of health-related data about a person and can be dynamically updated, are a key technology that can help guide medical decisions. Such medical digital twin models can be high-dimensional, multi-scale, and stochastic. To be practical for healthcare applications, they often need to be simplified into low-dimensional surrogate models that can be used for optimal design of interventions. This paper introduces surrogate modeling algorithms for the purpose of optimal control applications. As a use case, we focus on agent-based models (ABMs), a common model type in biomedicine for which there are no readily available optimal control algorithms. By deriving surrogate models that are based on systems of ordinary differential equations, we show how optimal control methods can be employed to compute effective interventions, which can then be lifted back to a given ABM. The relevance of the methods introduced here extends beyond medical digital twins to other complex dynamical systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
