Correlation of non-invasive parameters with upper gastrointestinal endoscopy findings for presence and grading of gastroesophageal varices in liver cirrhosis patients
- PMID: 38827664
- PMCID: PMC11141970
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_702_23
Correlation of non-invasive parameters with upper gastrointestinal endoscopy findings for presence and grading of gastroesophageal varices in liver cirrhosis patients
Abstract
Background: Development of esophageal varices is one of the major complications of liver cirrhosis, and endoscopy is used to see the presence, grading, and long-term monitoring of esophageal varices which is an invasive and unpleasant procedure. There is no adequate data available showing noninvasive methods can be used for the same.
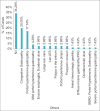
Methods: Seventy patients with liver cirrhosis participated in the study. Factors like portal vein diameter, spleen size, platelet count, serum bilirubin, Child-Pugh score, prothrombin time (PT), and PT INR were observed and correlated endoscopically with the presence and grading of esophageal varices in all patients.
Results: The platelet count, portal vein diameter, serum bilirubin, spleen bipolar diameter, and PT had statistically significant correlations with the presence of varices. Among them, platelet count, portal vein diameter, and serum bilirubin also had statistically significant correlations with the grading of varices. Monitoring of these noninvasive parameters can help in monitoring variceal growth.
Conclusions: Noninvasive parameters can be used effectively to predict the presence and grading of esophageal varices and at the same time keep the rate of undiagnosed varices acceptably low. By using noninvasive parameters, patients can be benefited by decreasing the requirement of repeated endoscopic evaluation which is an unpleasant procedure and availability is also limited.
Keywords: Esophageal varices; liver cirrhosis; platelet count; portal hypertension; portal vein diameter; spleen size; upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-Invasive Predictors of Gastro-Oesophageal Varices.JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2017 Jul-Sep;56(207):298-303. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29255309
-
Utilization of platelet count spleen diameter ratio in predicting the presence of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010 Feb;44(2):146-50. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181a745ff. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 19593164
-
Accuracy of non-endoscopic predictors of oesophageal varices in liver cirrhosis using platelet count, splenic size and portal vein diameter.Afr J Med Med Sci. 2016 Sep;45(3):243-251. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 29462529
-
[Non-invasive diagnosis of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Application to the primary prevention of varices].Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005 Oct;29(10):975-87. doi: 10.1016/s0399-8320(05)88170-9. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005. PMID: 16435503 Review. French.
-
Noninvasive scores for the prediction of esophageal varices and risk stratification in patients with cirrhosis.World J Hepatol. 2020 Nov 27;12(11):908-918. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i11.908. World J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33312418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schepis F, Cammà C, Niceforo D, Magnano A, Pallio S, Cinquegrani M. Which patients with cirrhosis should undergo endoscopic screening for esophageal varices detection? Hepatology. 2001;33:333–8. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico G, Luca A. Natural History. Clinical-haemodynamic correlations. Prediction of the risk of bleeding. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;11:243–56. - PubMed
-
- Christensen E, Fauerholdt L, Schlichting P, Juhl E, Poulsen H, Tygstrup N. Aspects of the natural history of gastrointestinal bleeding in cirrhosis and the effect of prednisone. Gastroenterology. 1981;81:944–52. - PubMed
-
- Pagliaro L, D’Amico G, Pasta L. Portal hypertension in cirrhosis: Natural history. In: Bosch J, Groszmann RJ, editors. Portal Hypertension: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1992. pp. 72–92.
-
- Merli M, Giorgia N, Stefania A. Incidence and natural history of small varices in cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol. 2003;38:266–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources