Dermatological Manifestation of SLE Patients, Living in Aseer Region
- PMID: 38827701
- PMCID: PMC11142007
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1234_23
Dermatological Manifestation of SLE Patients, Living in Aseer Region
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease that affects both men and women differently and has a variety of multisystemic symptoms. One of the diseases most often affected target organs is the skin. Different ethnic and racial groupings may display variations in disease incidence, clinical heterogeneity, and severity depending on environmental, cultural, or genetic factors. This study is conducted to determine the prevalence of SLE's cutaneous symptoms and their relationship to organ involvement.
Materials and methods: Data were gathered for this study from the patient chart, the study design was the retrospective chart review after the consent of the patients and obtaining an ethical approval, The study was carried out in Aseer Central Hospital, Abha Saudi Arabia.
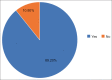
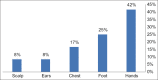
Results: Out of a total of 100 patients 92% were females while 8% were males. The mean (SD) of the age of the respondent was 38.3 (8.5). 89.2 of the respondents had skin manifestations.
Conclusion: A thorough understanding of SLE skin lesions will aid in the accurate identification of the condition and in the effective therapy of lupus patients. In order to more accurately diagnose cutaneous lesions in SLE patients, we need more dermatology and rheumatology clinics that combine expertise together.
Keywords: Dermatology; SLE; lupus; malar; rash; rheumatology.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus in a tertiary referral center.Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54(2):132-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.53189. Indian J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 20101308 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a Tertiary Center in Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2023 Jun 30;15(6):e41215. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41215. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37525814 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the Spectrum of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus with Disease Activity and Systemic Manifestations in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023 Sep 19;35(1):143-149. doi: 10.31138/mjr.200423.aos. eCollection 2024 Mar. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 38736948 Free PMC article.
-
Intersecting Realms of Skin and Neurology in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review of Dermatological and Neurological Manifestations and Their Impact on Long-Term Prognosis.Cureus. 2024 Jan 29;16(1):e53142. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53142. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38420059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for cutaneous disease in systemic lupus erythematosus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 9;3(3):CD007478. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007478.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33687069 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Skin Aging and the Upcoming Role of Ferroptosis in Geroscience.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 28;25(15):8238. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158238. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ghosh A. Cutaneous manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Indian J Rheumatol. 2007;2:156–64. doi:10.1016/S0973-3698(10)60060-X.
-
- Kalkhoran S, Benowitz NL, Rigotti NA. Reprint of: Prevention and treatment of tobacco use: JACC health promotion series. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72:2964–79. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2018.10.020. - PubMed
-
- Patel P, Werth V. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: A review. Dermatol Clin. 2002;20:373–85. v, doi:10.1016/s0733-8635(02)00016-5. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn A, Landmann A. The classification and diagnosis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2014;48(9):14–9. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.01.021. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn A, Sticherling M, Bonsmann G. Clinical manifestations of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2007;5:1124–37. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2007.06554.x. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources