HLA dependency and possible clinical relevance of intrathecally synthesized anti-IgLON5 IgG4 in anti-IgLON5 disease
- PMID: 38827736
- PMCID: PMC11141242
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1376456
HLA dependency and possible clinical relevance of intrathecally synthesized anti-IgLON5 IgG4 in anti-IgLON5 disease
Abstract
Background: Anti-IgLON5 disease is a rare chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by IgLON5 autoantibodies predominantly of the IgG4 subclass. Distinct pathogenic effects were described for anti-IgLON5 IgG1 and IgG4, however, with uncertain clinical relevance.
Methods: IgLON5-specific IgG1-4 levels were measured in 46 sera and 20 cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples from 13 HLA-subtyped anti-IgLON5 disease patients (six females, seven males) using flow cytometry. Intervals between two consecutive serum or CSF samplings (31 and 10 intervals, respectively) were categorized with regard to the immunomodulatory treatment active at the end of the interval, changes of anti-IgLON5 IgG1 and IgG4 levels, and disease severity. Intrathecal anti-IgLON5 IgG4 synthesis (IS) was assessed using a quantitative method.
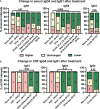
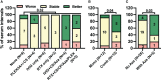
Results: The median age at onset was 66 years (range: 54-75), disease duration 10 years (range: 15-156 months), and follow-up 25 months (range: 0-83). IgLON5-specific IgG4 predominance was observed in 38 of 46 (83%) serum and 11 of 20 (55%) CSF samples. Anti-IgLON5 IgG4 levels prior clinical improvement in CSF but not serum were significantly lower than in those prior stable/progressive disease. Compared to IgLON5 IgG4 levels in serum, CSF levels in HLA-DRB1*10:01 carriers were significantly higher than in non-carriers. Indeed, IgLON5-specific IgG4 IS was demonstrated not only in four of five HLA-DRB1*10:01 carriers but also in one non-carrier. Immunotherapy was associated with decreased anti-IgGLON5 IgG serum levels. In CSF, lower anti-IgLON5 IgG was associated with immunosuppressive treatments used in combination, that is, corticosteroids and/or azathioprine plus intravenous immunoglobulins or rituximab.
Conclusion: Our findings might indicate that CSF IgLON5-specific IgG4 is frequently produced intrathecally, especially in HLA-DRB1*10:01 carriers. Intrathecally produced IgG4 may be clinically relevant. While many immunotherapies reduce serum IgLON5 IgG levels, more intense immunotherapies induce clinical improvement and may be able to target intrathecally produced anti-IgLON5 IgG. Further studies need to confirm whether anti-IgLON5 IgG4 IS is a suitable prognostic and predictive biomarker in anti-IgLON5 disease.
Keywords: HLA; IgG4; IgLON5; cerebrospinal fluid; intrathecal synthesis; therapy.
Copyright © 2024 Koneczny, Macher, Hutterer, Seifert-Held, Berger-Sieczkowski, Blaabjerg, Breu, Dreyhaupt, Dutra, Erdler, Fae, Fischer, Frommlet, Heidbreder, Högl, Klose, Klotz, Liendl, Nissen, Rahimi, Reinecke, Ricken, Stefani, Süße, Teive, Weis, Berger, Sabater, Gaig, Lewerenz and Höftberger.
Conflict of interest statement
TS-H reports travel grants and speaker honoraria from Roche. MBr has received honoraria for speaking from Sanofi. No conflict of interest with respect to the present study. AH reports speaker honoraria for UCB, Bioprojet, Servier, Medice, Jazz Pharmaceuticals BH reports speaker honoraria Jazz and Abbvie and advisor feed from Lundbeck. MS reports personal fees and grants from Merck Healthcare Deutschland and Bayer Vital GmbH and grant support from the University of Greifswald Gerhard-Domagk fellowship. HT reports speaker honoraria from Jansen, UCB and Zambon. TB has participated in meetings sponsored by and received honoraria lectures, advisory boards, consultations from pharmaceutical companies marketing treatments for MS: Allergan, Biogen, Biologix, Bionorica, BMS/Celgene, Eisei, Janssen-Cilag, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi-Genzyme, Teva, UCB. His institution has received financial support in the past 12 months by unrestricted research grants Bayer, Biogen, BMS/Celgene, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Teva and for participation in clinical trials in multiple sclerosis sponsored by Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, BMS/Celgene, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva. JL reports travel honoraria and speakers fees from the Cure Huntington’s Disease Initiative CHDI, the Movement Disorders Society as the German Society for Cerebrospinal Fluid Diagnostic and Clinical Neurochemistry DGLN. His institution received financial compensation for clinical trials with JL as principal investigator from CHDI. He is member of the executive board of the DGLN. He received research funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research BMBF. RH reports speaker honoraria from UCB and Biogen. The Medical University of Vienna Austria; employer of RH receives payment for antibody assays and for antibody validation experiments organized by Euroimmun Lübeck, Germany. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Sabater L, Gaig C, Gelpi E, Bataller L, Lewerenz J, Torres-Vega E, et al. . A novel non-rapid-eye movement and rapid-eye-movement parasomnia with sleep breathing disorder associated with antibodies to IgLON5: a case series, characterisation of the antigen, and post-mortem study. Lancet Neurol. (2014) 13:575–86. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70051-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

