Biochemistry of the Thrombin-Like Enzyme and Its Purification from Iranian Echis Carinatus Snake Venom: Its Interaction with Platelet Receptors
- PMID: 38828174
- PMCID: PMC11139400
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2023.78.6.1822
Biochemistry of the Thrombin-Like Enzyme and Its Purification from Iranian Echis Carinatus Snake Venom: Its Interaction with Platelet Receptors
Abstract
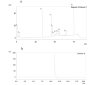
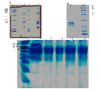
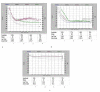
Snake venoms are rich in valuable substances that have medical potential in the diagnosis and treatment of hemostatic diseases. The present paper was aimed at the purification and functional characterization basis of a thrombin-like enzyme and its role in the functioning of the coagulation cascade and platelet aggregation pathway. A thrombin-like serine protease was purified from the Iranian Echis carinatus venom (TLIECV), employing a one-step chromatographic procedure. This peptide was collected in high yield and purity by a single chromatographic step using RP-HPLC equipped with a C18 column. This peptide showed a 3000 Da molecular weight in gel-electrophoresis. Evidence in the SDS-PAGE gel has confirmed high recovery of fraction in optimal terms. Subsequently, this peptide was identified via its intact molecular mass and peptide mass fingerprint (PMF) using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS). Multiple sequence alignments were performed by ClustalW, the Bioedit software. Molegro Data Modeller (MDM) 3.0 software was used to predict the putative tertiary structure of the peptide. The enzyme possessed fibrinogenolytic, procoagulant, and aggregation inducer properties. Moreover, the SDS-PAGE (12%) was applied to examine fibrinogenolytic function. The purified enzyme degraded the Aα chain of fibrinogen while the Bβ and γ chains were not digested. According to that, the deficient human plasma in factor X and normal human plasma were also coagulated by TLIECV, it takes part in the common and intrinsic routes of the coagulation cascade. These findings proved that TLIECV is a serine protease identical to procoagulant thrombin-like snake venom proteases; however, it specifically releases the Aα chain of bovine fibrinogen. Because of its function to make up for the deficiency of factor X and its platelet aggregation inducer property, TLIECV could be considered a molecular impact to reveal the hemostasis mechanisms.
Keywords: Blood coagulation; Platelet aggregation inducer; Platelet function; Snake venom; Thrombin-like.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analysis and Identification of Putative Novel Peptides Purified from Iranian Endemic Echis Carinatus Sochureki Snake Venom by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry.Arch Razi Inst. 2023 Oct 31;78(5):1503-1527. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2023.78.5.1503. eCollection 2023 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2023. PMID: 38590689 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of a thrombin-like enzyme isolated from Vipera lebetina venom: its interaction with platelet receptor.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2020 Jan;31(1):1-10. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000856. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2020. PMID: 31764002
-
Molecular cloning and expression of a functional snake venom serine proteinase, with platelet aggregating activity, from the Cerastes cerastes viper.Biochemistry. 2003 Sep 16;42(36):10609-18. doi: 10.1021/bi034790b. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12962484
-
Snake venoms and the hemostatic system.Toxicon. 1998 Dec;36(12):1749-800. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(98)00126-3. Toxicon. 1998. PMID: 9839663 Review.
-
[Thrombin-like serine proteases in Cerasted venoms (Cerasted cerastes and Cerastes vipera)].Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis. 1998 Jan-Apr;75(1-2):3-8. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis. 1998. PMID: 14722941 Review. French.
References
-
- Kadi-Saci A, Laraba-Djebari F. Purification and characterization of a thrombin-like enzyme isolated from Vipera lebetina venom: its interaction with platelet receptor. Blood coagulation & fibrinolysis : an international journal in haemostasis and thrombosis. 2020;31(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Damotharan P, Veeruraj A, Arumugam M, Balasubramanian T. Isolation and characterization of biologically active venom protein from sea snake Enhydrina schistosa. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology. 2015;29(3):140–7. - PubMed
-
- Ullah A, Masood R, Ali I, Ullah K, Ali H, Akbar H, et al. Thrombin-like enzymes from snake venom: Structural characterization and mechanism of action. International journal of biological macromolecules. 2018;114:788–811. - PubMed
-
- Bell WR., Jr Defibrinogenating enzymes. Drugs. 1997;54 Suppl 3:18–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
