The Effects of Melatonin Alone or in Combination with Zinc on Gonadotropin and Thyroid Hormones in Female Rats
- PMID: 38828181
- PMCID: PMC11139389
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2023.78.6.1698
The Effects of Melatonin Alone or in Combination with Zinc on Gonadotropin and Thyroid Hormones in Female Rats
Abstract
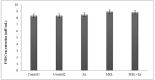
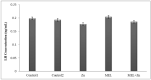
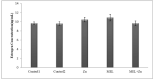
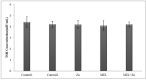
Thyroid and gonadotropin hormones play an essential role in the regulation of regulating various physiological functions. The effects of melatonin and zinc (Zn) on these hormones have already been investigated. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of melatonin with and without zinc on the levels of gonadotropin hormones and thyroid hormones (triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)) in female rats. In general, 35 sexually mature female rats were randomly divided into five treatment groups, with each group comprising 7 rats, in a completely randomized design (CRD) during the research. The rats were treated daily with Zn and melatonin via gavage as follows T1 (control 1, basal diet), T2 (control 2, treatment with normal saline) and the other experimental groups, including T3, T4 and T5, were treated with Zn (40 ppm), melatonin (5 mg/kg) or a combination of Zn and melatonin at the same dose. The administration of the drugs was continued for 20 days (daily) . Plasma samples were then taken for the determination of LH, FFH, LH/FSH, estrogen, progesterone, T3, T4 and TSH levels. The results showed no significant differences in FSH and LH levels between treatments. Estrogen, progesterone and TSH levels were higher in the rats receiving 5 mg melatonin per day than in the other groups, but not statistically significant (P>0.05). However, T3 levels decreased significantly in the group receiving 40 mg/kg Zn compared to the other experiments. (P<0.05). The results showed no significant difference between the treatments in terms of T4 levels (P>0.05). In conclusion, no remarkable changes in other variables were observed in female rats receiving melatonin, Zn or a combination of melatonin and Zn, with the exception of T3.
Keywords: Estrogen; Female rat; Melatonin; Progesterone; T3; T4; TSH; Zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The writers declare to the fact that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


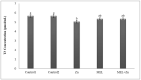
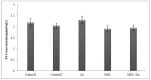
References
-
- Li Y, Yin Z, Zhang Y, Liu J, Cheng Y, Wang J, Pi F, Zhang Y, Sun X. Perspective of Microbe-based Minerals Fortification in Nutrition Security. Food Rev. Int. 2022;38(3):268–81.
-
- Harlow HJ. Influence of the pineal gland and melatonin on blood flow and evaporative water loss during heat stress in rats. J Pineal Res. 1987;4(2):147–59. - PubMed
-
- Bonior J, Jaworek J, Konturek SJ, Pawlik WW. Increase of heat shock protein gene expression by melatonin in AR42J cells. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005;56(3):471. - PubMed
-
- Vittorio U, Emanuela R, Piero R, Silvia B. Effect of a supplementation with myo-inositol plus melatonin on oocyte quality in women who failed to conceive in previousin vitrofertilization cycles for poor oocyte quality: a prospective, longitudinal, cohort study. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2011;27(11):857–61. - PubMed
-
- Lampiao F, Du Plessis SS. New developments of the effect of melatonin on reproduction. World J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;10;2(2):8–15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
