Engineered Exosomes Containing microRNA-29b-2 and Targeting the Somatostatin Receptor Reduce Presenilin 1 Expression and Decrease the β-Amyloid Accumulation in the Brains of Mice with Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38828204
- PMCID: PMC11144417
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S442876
Engineered Exosomes Containing microRNA-29b-2 and Targeting the Somatostatin Receptor Reduce Presenilin 1 Expression and Decrease the β-Amyloid Accumulation in the Brains of Mice with Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Purpose: Exosomes are membrane vesicles secreted by various cells and play a crucial role in intercellular communication. They can be excellent delivery vehicles for oligonucleotide drugs, such as microRNAs, due to their high biocompatibility. MicroRNAs have been shown to be more stable when incorporated into exosomes; however, the lack of targeting and immune evasion is still the obstacle to the use of these microRNA-containing nanocarriers in clinical settings. Our goal was to produce functional exosomes loaded with target ligands, immune evasion ligand, and oligonucleotide drug through genetic engineering in order to achieve more precise medical effects.
Methods: To address the problem, we designed engineered exosomes with exogenous cholecystokinin (CCK) or somatostatin (SST) as the targeting ligand to direct the exosomes to the brain, as well as transduced CD47 proteins to reduce the elimination or phagocytosis of the targeted exosomes. MicroRNA-29b-2 was the tested oligonucleotide drug for delivery because our previous research showed that this type of microRNA was capable of reducing presenilin 1 (PSEN1) gene expression and decreasing the β-amyloid accumulation for Alzheimer's disease (AD) in vitro and in vivo.
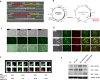
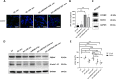
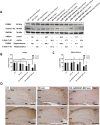
Results: The engineered exosomes, containing miR29b-2 and expressing SST and CD47, were produced by gene-modified dendritic cells and used in the subsequent experiments. In comparison with CD47-CCK exosomes, CD47-SST exosomes showed a more significant increase in delivery efficiency. In addition, CD47-SST exosomes led to a higher delivery level of exosomes to the brains of nude mice when administered intravenously. Moreover, it was found that the miR29b-2-loaded CD47-SST exosomes could effectively reduce PSEN1 in translational levels, which resulted in an inhibition of beta-amyloid oligomers production both in the cell model and in the 3xTg-AD animal model.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated the feasibility of the designed engineered exosomes. The application of this exosomal nanocarrier platform can be extended to the delivery of other oligonucleotide drugs to specific tissues for the treatment of diseases while evading the immune system.
Keywords: 3xTG-AD; SH-SY5Y; functional nanocarriers; hippocampus; oligonucleotide drug.
© 2024 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting PSEN1 by lnc-CYP3A43-2/miR-29b-2-5p to Reduce β Amyloid Plaque Formation and Improve Cognition Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 11;23(18):10554. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810554. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142465 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-mediated augmented exosome release from astrocytes alleviates amyloid-β-induced neurotoxicity.Theranostics. 2021 Feb 25;11(9):4351-4362. doi: 10.7150/thno.52436. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33754065 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Dynamics and miRNA Signaling Differ between SH-SY5Y APPSwe and PSEN1 Mutant iPSC-Derived AD Models upon Modulation with miR-124 Mimic and Inhibitor.Cells. 2021 Sep 14;10(9):2424. doi: 10.3390/cells10092424. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572073 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-1 mutation is associated with a hippocampus defect in alzheimer's disease: Meta-Analysis for neuroimaging research.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Apr;191:105679. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105679. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32004985
-
Camouflage strategies for therapeutic exosomes evasion from phagocytosis.J Adv Res. 2021 Jan 8;31:61-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.01.001. eCollection 2021 Jul. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 34194832 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles in Neurodegenerative Disease: Emerging Roles in Pathogenesis, Biomarker Discovery, and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 26;26(15):7246. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157246. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes enriched with miR-124-3p show therapeutic potential in a new microfluidic triculture model that recapitulates neuron-glia crosstalk in Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 12;16:1474012. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1474012. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40144670 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes as nanocarriers for brain-targeted delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids: advances and challenges.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jun 18;23(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03528-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40533746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles as drug and gene delivery vehicles in central nervous system diseases.Biomater Sci. 2025 Feb 25;13(5):1161-1178. doi: 10.1039/d4bm01394h. Biomater Sci. 2025. PMID: 39871579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Research on Exosomal miRNAs in Central Nervous System Diseases.ASN Neuro. 2025;17(1):2465546. doi: 10.1080/17590914.2025.2465546. Epub 2025 Apr 1. ASN Neuro. 2025. PMID: 40165664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia. Accessed March 15, 2023.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

