How social support and resilience impact mental health: The moderating role of time in isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 38828315
- PMCID: PMC11140785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31783
How social support and resilience impact mental health: The moderating role of time in isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
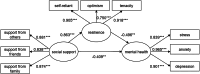
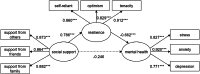
During the COVID-19 pandemic, quarantines effectively prevented the spread of COVID-19 but also caused people to develop mental health problems. We thus aimed to verify the impact of social support and resilience on mental health and to uncover the moderating role played by time in isolation during the post-pandemic era. We administered a cross-sectional survey to 510 college students. The results found that social support directly and negatively predicted mental health problems, and this relationship was mediated by resilience. Through multigroup analysis, resilience partially mediated the relationship between social support and mental health during period of isolation 1 (PI1) and fully mediated this relationship during period of isolation 2 (PI2) and period of isolation 3 (PI3). Moreover, the path coefficient of resilience to mental health at T3 was significantly higher than that at T2. Thus, the effect of resilience on mental health increases with the duration of time in isolation.
Keywords: Mental health; Multi-group analysis; Resilience; Social support; Time in isolation.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of social support on home isolation anxiety and depression among college students in the post-pandemic era: the mediating effect of perceived loss of control and the moderating role of family socioeconomic status.Front Public Health. 2024 Feb 9;12:1288848. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1288848. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38406501 Free PMC article.
-
The Fully Mediating Role of Psychological Resilience between Self-Efficacy and Mental Health: Evidence from the Study of College Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Feb 1;11(3):420. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030420. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766995 Free PMC article.
-
The Indirect Impact of Educational Attainment as a Distal Resource for Older Adults on Loneliness, Social Isolation, Psychological Resilience, and Technology Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Cross-Sectional Quantitative Study.JMIR Aging. 2023 Nov 24;6:e47729. doi: 10.2196/47729. JMIR Aging. 2023. PMID: 37999938 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Related Stress and Mental Health Outcomes 1 Year After the Peak of the Pandemic Outbreak in China: the Mediating Effect of Resilience and Social Support.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 21;13:828379. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.828379. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35264988 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Fear of the COVID-19 on Depression Among Chinese Outbound Students Studying Online in China Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic Period: The Role of Resilience and Social Support.Front Psychol. 2021 Oct 15;12:750011. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.750011. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34721231 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
'Let the System Do Its Job and Families Handle the Rest'? Protective and Risk Factors Contributing to Pandemic Crisis Parental Burnout.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 18;14(2):617. doi: 10.3390/jcm14020617. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39860623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laslo-Roth R., George-Levi S., Margalit M. Hope during the covid-19 outbreak: coping with the psychological impact of quarantine. Counsell. Psychol. Q. 2021;34(3–4):771–785. doi: 10.1080/09515070.2021.1881762. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous