Sport tourist perceptions of destination image and revisit intentions: An adaption of Mehrabian-Russell's environmental psychology model
- PMID: 38828342
- PMCID: PMC11140795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31810
Sport tourist perceptions of destination image and revisit intentions: An adaption of Mehrabian-Russell's environmental psychology model
Abstract
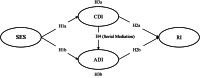
In environmental psychology literature, an individual's perception of the surroundings leads to subsequent behaviors. In this regard, small-scale sport events (SSE) have been used as a marketing tool for tourism development. However, how SSEs are leveraged to improve destination image (DI) for tourists has not been fully understood. Building on Mehrabian-Russell's environmental psychology model, this study examined the relationship between the SSE environmental stimuli and revisit intentions through the sequential mediation of cognitive and affective DI. Data from the 423 respondents were collected from 2023 Wuxi Marathon held in Wuxi, China. Structural equation modeling was employed to analyze the hypothesized framework. The results indicated that the SSE environmental stimuli were positively associated with both cognitive and affective DI, which were positively correlated with revisit intentions. The applicability of the serial mediation of cognitive and affective DI within the relationship was confirmed. This study contributes to the sport and tourism literature by extending the applicability of Mehrabian and Russell's model to SSE settings and identifying the serial mediating effects of cognitive and affective DI.
Keywords: Affective destination image; Cognitive destination image; Environmental stimuli; Revisit intention; Sport tourism.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Ji Wu reports financial support was provided by Shanghai Pujiang Program. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Afshardoost M., Eshaghi M.S. Destination image and tourist behavioural intentions: a meta-analysis. Tourism Manag. 2020;81 doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2020.104154. - DOI
-
- Alexandris K., Kaplanidou K. Marketing sport event tourism: sport tourist behaviors and destination provisions. Sport Market. Q. 2014;23:125–127.
-
- Chalip L., Green B.C., Hill B. Effects of sport event media on destination image and intention to visit. J. Sport Manag. 2003;17:214–234. doi: 10.1123/jsm.17.3.214. - DOI
-
- Gibson H.J., Qi C.X., Zhang J.J. Destination image and intent to visit China and the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. J. Sport Manag. 2008;22:427–450. doi: 10.1123/jsm.22.4.427. - DOI
-
- Kelly D.M., Fairley S. What about the event? How do tourism leveraging strategies affect small-scale events? Tourism Manag. 2018;64:335–345. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2017.09.009. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

