LP340, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, decreases liver injury and fibrosis in mice: role of oxidative stress and microRNA-23a
- PMID: 38828459
- PMCID: PMC11140137
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1386238
LP340, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, decreases liver injury and fibrosis in mice: role of oxidative stress and microRNA-23a
Abstract
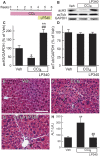
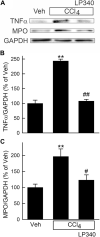
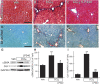
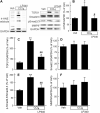
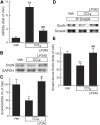
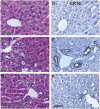
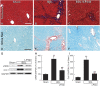
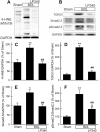
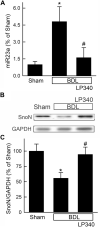
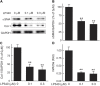
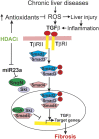
Effective therapy for liver fibrosis is lacking. Here, we examined whether LP340, the lead candidate of a new-generation of hydrazide-based HDAC1,2,3 inhibitors (HDACi), decreases liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis was induced by CCl4 treatment and bile duct ligation (BDL) in mice. At 6 weeks after CCl4, serum alanine aminotransferase increased, and necrotic cell death and leukocyte infiltration occurred in the liver. Tumor necrosis factor-α and myeloperoxidase markedly increased, indicating inflammation. After 6 weeks, α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) and collagen-1 expression increased by 80% and 575%, respectively, indicating hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and fibrogenesis. Fibrosis detected by trichrome and Sirius-red staining occurred primarily in pericentral regions with some bridging fibrosis in liver sections. 4-Hydroxynonenal adducts (indicator of oxidative stress), profibrotic cytokine transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ), and TGFβ downstream signaling molecules phospho-Smad2/3 also markedly increased. LP340 attenuated indices of liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis markedly. Moreover, Ski-related novel protein-N (SnoN), an endogenous inhibitor of TGFβ signaling, decreased, whereas SnoN expression suppressor microRNA-23a (miR23a) increased markedly. LP340 (0.05 mg/kg, ig., daily during the last 2 weeks of CCl4 treatment) decreased 4-hydroxynonenal adducts and miR23a production, blunted SnoN decreases, and inhibited the TGFβ/Smad signaling. By contrast, LP340 had no effect on matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. LP340 increased histone-3 acetylation but not tubulin acetylation, indicating that LP340 inhibited Class-I but not Class-II HDAC in vivo. After BDL, focal necrosis, inflammation, ductular reactions, and portal and bridging fibrosis occurred at 2 weeks, and αSMA and collagen-1 expression increased by 256% and 560%, respectively. LP340 attenuated liver injury, ductular reactions, inflammation, and liver fibrosis. LP340 also decreased 4-hydroxynonenal adducts and miR23a production, prevented SnoN decreases, and inhibited the TGFβ/Smad signaling after BDL. In vitro, LP340 inhibited immortal human hepatic stellate cells (hTERT-HSC) activation in culture (αSMA and collagen-1 expression) as well as miR23a production, demonstrating its direct inhibitory effects on HSC. In conclusions, LP340 is a promising therapy for both portal and pericentral liver fibrosis, and it works by inhibiting oxidative stress and decreasing miR23a.
Keywords: SnoN; TGFβ; histone deacetylase; liver fibrosis; microRNA-23a; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2024 Samuvel, Lemasters, Chou and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
CC is the co-founder of Lydex Pharmaceuticals where LP340 was synthesized. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sinomenine Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Blocking TGF-β/SMAD and c-JUN Signaling.Phytother Res. 2025 Jul;39(7):3182-3196. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8502. Epub 2025 Jun 1. Phytother Res. 2025. PMID: 40452107
-
Aramchol attenuates fibrosis in mouse models of biliary fibrosis and blocks the TGFβ-induced fibroinflammatory mediators in cholangiocytes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 13:2024.11.06.621880. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.06.621880. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Hepatol Commun. 2025 Jul 29;9(8):e0748. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000748. PMID: 39574583 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tanshinone IIA attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation, oxidative stress, and liver fibrosis by inhibiting YAP signaling.Eur J Histochem. 2025 Jun 17;69(3):4218. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2025.4218. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Eur J Histochem. 2025. PMID: 40525818 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiators (specific therapies for class III and IV mutations) for cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 26;(3):CD009841. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009841.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 07;1:CD009841. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009841.pub3. PMID: 25811419 Updated.
Cited by
-
Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 15;14(12):1605. doi: 10.3390/biom14121605. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

