SIRT1 mediates the excitability of spinal CaMKIIα-positive neurons and participates in neuropathic pain by controlling Nav1.3
- PMID: 38828629
- PMCID: PMC11145124
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.14764
SIRT1 mediates the excitability of spinal CaMKIIα-positive neurons and participates in neuropathic pain by controlling Nav1.3
Abstract
Aims: Neuropathic pain is a common chronic pain disorder, which is largely attributed to spinal central sensitization. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alpha (CaMKIIα) activation in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH) is a major contributor to spinal sensitization. However, the exact way that CaMKIIα-positive (CaMKIIα+) neurons in the SDH induce neuropathic pain is still unclear. This study aimed to explore the role of spinal CaMKIIα+ neurons in neuropathic pain caused by chronic constriction injury (CCI) and investigate the potential epigenetic mechanisms involved in CaMKIIα+ neuron activation.
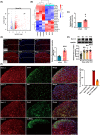
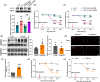
Methods: CCI-induced neuropathic pain mice model, Sirt1loxP/loxP mice, and chemogenetic virus were used to investigate whether the activation of spinal CaMKIIα+ neurons is involved in neuropathic pain and its involved mechanism. Transcriptome sequence, western blotting, qRT-PCR, and immunofluorescence analysis were performed to assay the expression of related molecules and activation of neurons. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to observe the binding relationship of protein. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-PCR was applied to analyze the acetylation of histone H3 in the Scn3a promoter region.
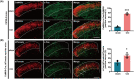
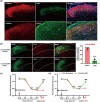
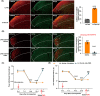
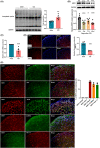
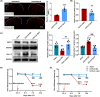
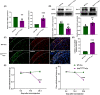
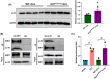
Results: The expression of sodium channel Nav1.3 was increased and the expression of SIRT1 was decreased in the spinal CaMKIIα+ neurons of CCI mice. CaMKIIα neurons became overactive after CCI, and inhibiting their activation relieved CCI-induced pain. Overexpression of SIRT1 reversed the increase of Nav1.3 and alleviated pain, while knockdown of SIRT1 or overexpression of Nav1.3 promoted CaMKIIα+ neuron activation and induced pain. By knocking down spinal SIRT1, the acetylation of histone H3 in the Scn3a (encoding Nav1.3) promoter region was increased, leading to an increased expression of Nav1.3.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that an aberrant reduction of spinal SIRT1 after nerve injury epigenetically increases Nav1.3, subsequently activating CaMKIIα+ neurons and causing neuropathic pain.
Keywords: CaMKIIα+ neurons; Nav1.3; SIRT1; neuropathic pain.
© 2024 The Author(s). CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NaHS alleviates neuropathic pain in mice by inhibiting IL-17-mediated dopamine (DA) neuron necroptosis in the VTA.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Jan;220:111168. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111168. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39672209
-
Increased NaV1.2 expression and its interaction with CaM contribute to the hyperexcitability induced by prolonged inhibition of CaMKII.Epilepsia. 2025 Jul;66(7):2521-2537. doi: 10.1111/epi.18377. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Epilepsia. 2025. PMID: 40119845
-
EGR2 maintains neuropathic pain by promoting microglial phagocytosis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Apr 28;50(4):586-601. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2025.240270. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40785673 Free PMC article.
-
Venlafaxine for neuropathic pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 23;2015(8):CD011091. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011091.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26298465 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal activation of spinal glial cells: role of gliopathy in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury in rats.Exp Neurol. 2012 Apr;234(2):362-72. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.10.010. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22036747 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
5-HT1AR agonist alleviates presurgical prolonged sleep deprivation-induced postsurgical pain in adolescent mice.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 28;49(10):1543-1555. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240499. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40074303 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Sirtuin1 in Spinal Cord Injury: Regulatory Mechanisms, Microenvironment Remodeling and Therapeutic Potential.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Feb;31(2):e70244. doi: 10.1111/cns.70244. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39915897 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of traditional Chinese medicine in treating neuropathic pain.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 3;10(17):e37350. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37350. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39296122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overactive PKA signaling underlies the hyperalgesia in an ADHD mouse model.iScience. 2024 Oct 5;27(11):111110. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111110. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39507260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister K, Sachau J, Baron R, Dickenson AH. Neuropathic pain: mechanism‐based therapeutics. In: Insel PA, ed. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Vol 60. Annual Reviews Inc.; 2020:257‐274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

