The translocation activity of Rad54 reduces crossover outcomes during homologous recombination
- PMID: 38828785
- PMCID: PMC11229335
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae474
The translocation activity of Rad54 reduces crossover outcomes during homologous recombination
Abstract
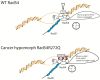
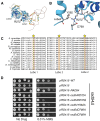
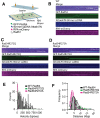
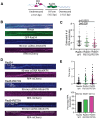
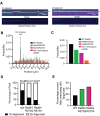
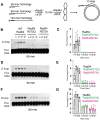
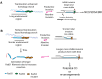
Homologous recombination (HR) is a template-based DNA double-strand break repair pathway that requires the selection of an appropriate DNA sequence to facilitate repair. Selection occurs during a homology search that must be executed rapidly and with high fidelity. Failure to efficiently perform the homology search can result in complex intermediates that generate genomic rearrangements, a hallmark of human cancers. Rad54 is an ATP dependent DNA motor protein that functions during the homology search by regulating the recombinase Rad51. How this regulation reduces genomic exchanges is currently unknown. To better understand how Rad54 can reduce these outcomes, we evaluated several amino acid mutations in Rad54 that were identified in the COSMIC database. COSMIC is a collection of amino acid mutations identified in human cancers. These substitutions led to reduced Rad54 function and the discovery of a conserved motif in Rad54. Through genetic, biochemical and single-molecule approaches, we show that disruption of this motif leads to failure in stabilizing early strand invasion intermediates, causing increased crossovers between homologous chromosomes. Our study also suggests that the translocation rate of Rad54 is a determinant in balancing genetic exchange. The latch domain's conservation implies an interaction likely fundamental to eukaryotic biology.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functions of the Snf2/Swi2 family Rad54 motor protein in homologous recombination.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Sep;1809(9):509-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.06.006. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21704205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro role of Rad54 in Rad51-ssDNA filament-dependent homology search and synaptic complexes formation.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 6;10(1):4058. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12082-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31492866 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Dmc1 and Rad51 proteins preferentially function with Tid1 and Rad54 proteins, respectively, to promote DNA strand invasion during genetic recombination.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 17;287(34):28727-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.373290. Epub 2012 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22761450 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hed1 and Rad54 binding during maturation of the meiosis-specific presynaptic complex.EMBO J. 2018 Apr 3;37(7):e98728. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798728. Epub 2018 Feb 14. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29444896 Free PMC article.
-
Discrete roles for Rad54 and Rdh54 during homologous recombination.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021 Dec;71:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2021.06.013. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021. PMID: 34293661 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for Rad54- and Hed1-mediated regulation of Rad51 during the transition from mitotic to meiotic recombination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 26:2025.03.26.645561. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.26.645561. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40196570 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

