Vandetanib in locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine therapy
- PMID: 38828895
- PMCID: PMC11301419
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-23-0354
Vandetanib in locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer refractory to radioiodine therapy
Abstract
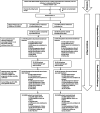
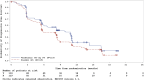
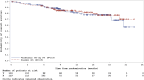
The VERIFY study aimed to determine the efficacy of vandetanib in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) that is either locally advanced or metastatic and refractory to radioiodine (RAI) therapy. Specifically, VERIFY is a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase III trial aimed to determine the efficacy and safety of vandetanib in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-naive patients with locally advanced or metastatic RAI-refractory DTC with documented progression (NCT01876784). Patients were randomized 1:1 to vandetanib or placebo. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). Secondary endpoints included best objective response rate, overall survival (OS), safety, and tolerability. Patients continued to receive randomized treatment until disease progression or for as long as they were receiving clinical benefit unless criteria for treatment discontinuation were met. Following randomization, 117 patients received vandetanib, and 118 patients received a placebo. Median PFS was 10.0 months in the vandetanib group and 5.7 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.55-1.03; P = 0.080). OS was not significantly different between treatment arms. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) of grade ≥3 were reported in 55.6% of patients in the vandetanib arm and 25.4% in the placebo arm. Thirty-three deaths (28.2%; one related to study treatment) occurred in the vandetanib arm compared with 16 deaths (13.6%; two related to treatment) in the placebo arm. No statistically significant improvement was observed in PFS in treatment versus placebo in patients with locally advanced or metastatic, RAI-refractory DTC. Moreover, active treatment was associated with more adverse events and more deaths than placebo, though the difference in OS was not statistically significant.
Keywords: differentiated thyroid cancer; multikinase inhibitor; progression-free survival; radioiodine refractory; vandetanib.
Conflict of interest statement
MSB has received honoraria for scientific consultancy (advisory roles) and trial funding from Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Bayer Healthcare, Loxo Oncology, Eisai, and Novartis. LB has received honoraria for scientific consultancy roles (speaker and advisory roles) from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Roche, Ipsen, Bayer, Eisai, Amgen, and AstraZeneca. JB was an employee of Sanofi at the time of this analysis. JC has received honoraria for scientific consultancy roles (speaker and advisory roles) from Novartis, Pfizer, Ipsen, Exelixis, Bayer, Eisai, Advanced Accelerator Applications, Amgen, Sanofi, and Merck Serono, and research support from Eisai, Novartis, Ipsen, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, and Advanced Accelerator Applications. RMC is an employee of Sanofi. PC is an employee of Sanofi and a Sanofi stock shareholder. RE is a consultant for Eisai, Sanofi, Exelixis, and Loxo Oncology. DF-S has received honoraria for scientific consultancy roles (speaker and advisory roles) from Novartis, Pfizer, Ipsen, Bayer, Eisai, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Sanofi, and Merck Serono, and research support from Novartis, Ipsen, and Pfizer. SLe is a consultant for Eisai, Sanofi, Bayer, and Loxo Oncology. SLi is a Sanofi employee and Sanofi stock shareholder. IS has received honoraria for scientific consultancy roles (speaker and advisory roles) from Bayer and Eisai, and research support from Eisai. MHT received fees for consulting/advisory board participation for Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai Inc., Blueprint Medicines, Loxo Oncology, Bayer, Array Biopharma, Arqule, and Novartis, and unbranded speaking engagements with Bristol-Myers Squibb and Eisai Inc. ZW has no conflicts to disclose. LJW has received honoraria for scientific consultancy from Bayer, Eisai, Loxo Oncology, and Merck. FPW has received honoraria for scientific consultancy from Bayer, CUE Biopharmaceuticals, Fusion Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Loxo Oncology, and Merck. MS has received consulting fees and research grants from Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis-IPSEN, and Sanofi. MS is on the editorial board of
Figures


References
-
- Brose MS, Nutting CM, Jarzab B, Elisei R, Siena S, Bastholt L, de la Fouchardiere C, Pacini F, Paschke R, Shong YK, et al.2014Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 384319–328. ( 10.1016/S0140-6736(1460421-9) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Robinson B, Sherman SI, Krajewska J, Lin CC, Vaisman F, Hoff AO, Hitre E, Bowles DW, Hernando J, et al.2021Cabozantinib for radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (COSMIC-311): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncology 221126–1138. ( 10.1016/S1470-2045(2100332-6) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Doebele RC, Drilon A, Paz-Ares L, Siena S, Shaw AT, Farago AF, Blakely CM, Seto T, Cho BC, Tosi D, et al.2020Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: integrated analysis of three phase 1-2 trials. Lancet. Oncology 21271–282. ( 10.1016/S1470-2045(1930691-6) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Durante C, Haddy N, Baudin E, Leboulleux S, Hartl D, Travagli JP, Caillou B, Ricard M, Lumbroso JD, De Vathaire F, et al.2006Long-term outcome of 444 patients with distant metastases from papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma: benefits and limits of radioiodine therapy. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 912892–2899. ( 10.1210/jc.2005-2838) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

