Differential regulation of STARD1, STARD4 and STARD6 in the human ovary
- PMID: 38829257
- PMCID: PMC11267794
- DOI: 10.1530/JOE-23-0385
Differential regulation of STARD1, STARD4 and STARD6 in the human ovary
Abstract
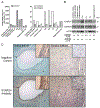
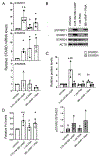
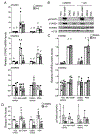
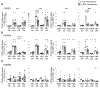
Cells actively engaged in de novo steroidogenesis rely on an expansive intracellular network to efficiently transport cholesterol. The final link in the transport chain is STARD1, which transfers cholesterol to the enzyme complex that initiates steroidogenesis. However, the regulation of ovarian STARD1 is not fully characterized, and even less is known about the upstream cytosolic cholesterol transporters STARD4 and STARD6. Here, we identified both STARD4 and STARD6 mRNAs in the human ovary but only detected STARD4 protein since the primary STARD6 transcript turned out to be a splice variant. Corpora lutea contained the highest levels of STARD4 and STARD1 mRNA and STARD1 protein, while STARD4 protein was uniformly distributed across ovarian tissues. Cyclic AMP analog (8Br-cAMP) and phorbol ester (PMA) individually increased STARD1 and STARD4 mRNA along with STARD1 protein and its phosphoform in cultured primary human luteinized granulosa cells (hGCs). STARD6 transcripts and STARD4 protein were unresponsive to these stimuli. Combining lower doses of PMA and 8Br-cAMP blunted the 8Br-cAMP stimulation of STARD1 protein. Increasing cholesterol levels by blocking its conversion to steroid with aminoglutethimide or by adding LDL reduced the STARD4 mRNA response to stimuli. Sterol depletion reduced the STARD1 mRNA and protein response to PMA. These data support a possible role for STARD4, but not STARD6, in supplying cholesterol for steroidogenesis in the ovary. We demonstrate for the first time how cAMP, PMA and sterol pathways separately and in combination differentially regulate STARD4, STARD6 and STARD1 mRNA levels, as well as STARD1 and STARD4 protein in human primary ovarian cells.
Keywords: START domain; cholesterol; human; luteinized granulosa; progesterone.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
STARD6 is expressed in steroidogenic cells of the ovary and can enhance de novo steroidogenesis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 Apr;239(4):430-5. doi: 10.1177/1535370213517616. Epub 2014 Mar 4. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014. PMID: 24595982 Free PMC article.
-
Period circadian regulator 2-mediated steroid hormone synthesis by regulating transcription of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in porcine granulosa cells.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae185. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae185. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38982717 Free PMC article.
-
StAR-like activity and molten globule behavior of StARD6, a male germ-line protein.Biochemistry. 2008 Feb 26;47(8):2277-88. doi: 10.1021/bi701966a. Epub 2008 Jan 23. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18211099
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between Advanced Glycation End Products and Steroidogenesis in PCOS.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Oct 21;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12958-016-0205-6. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27769286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome.Endocr Connect. 2025 Jul 12;14(7):e250186. doi: 10.1530/EC-25-0186. Print 2025 Jul 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40586348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arakane F, King SR, Du Y, Kallen CB, Walsh LP, Watari H, Stocco DM & Strauss JF III 1997. Phosphorylation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) modulates its steroidogenic activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 32656–32662. - PubMed
-
- Bogan RL & Niswender GD 2007. Constitutive steroidogenesis in ovine large luteal cells may be mediated by tonically active protein kinase A. Biology of Reproduction 77 209–216. - PubMed
-
- Bose HS, Whittal RM, Ran Y, Bose M, Baker BY & Miller WL 2008. StAR-like activity and molten globule behavior of StARD6, a male germ-line protein. Biochemistry 47 2277–2288. - PubMed
-
- Chin EC, Harris TE & Abayasekara DR 2004. Changes in cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and progesterone secretion in luteinizing human granulosa cells. Journal of Endocrinology 183 39–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

