Adherence to Current Dyslipidemia Guideline in Patients Utilizing Statins According to Risk Groups and Gender Differences: The AIZANOI Study
- PMID: 38829258
- PMCID: PMC11168716
- DOI: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2024.4218
Adherence to Current Dyslipidemia Guideline in Patients Utilizing Statins According to Risk Groups and Gender Differences: The AIZANOI Study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the adherence to the current European Society of Cardiology dyslipidemia guidelines, the ratio of reaching target values according to risk groups, and the reasons for not reaching LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) goals in patients on already statin therapy in a cardiology outpatient population.
Methods: The AIZANOI study is a multi-center, cross-sectional observational study including conducted in 9 cardiology centers between August 1, 2021, and November 1, 2021.
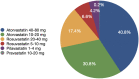
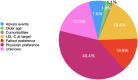
Results: A total of 1225 patients (mean age 62 ± 11 years, 366 female) who were already on statin therapy for at least 3 months were included. More than half (58.2%) of the patients were using high-intensity statin regimens. Only 26.2% of patients had target LDL-C level according to their risk score. Despite 58.4% of very high-risk patients and 44.4% of high-risk patients have been using a high-intensity statin regimen, only 24.5% of very-high-risk patients and only 34.9% of high-risk patients have reached guideline-recommended LDL-C levels. Most prevalent reason for not using target dose statin was physician preference (physician inertia) (40.3%).
Conclusion: The AIZANOI study showed that we achieved a target LDL-C level in only 26.2% of patients using statin therapy. Although 58.4% of patients with a very high SCORE risk and 44.4% of patients with a high SCORE risk were using a target dose statin regimen, we were only able to achieve guideline-recommended LDL-C levels in 24.5% and 34.9% of them, respectively, in cardiology outpatients clinics. Physician inertia is one of the major factors in non-adherence to guidelines. These findings highlight that combination therapy is needed in most of the patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Borén J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(24):2313 2330. (10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ference BA, Ginsberg HN, Graham I, et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(32):2459 2472. (10.1093/eurheartj/ehx144) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical