Effect of a multicomponent quality improvement strategy on sustained achievement of diabetes care goals and macrovascular and microvascular complications in South Asia at 6.5 years follow-up: Post hoc analyses of the CARRS randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 38829880
- PMCID: PMC11198027
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004335
Effect of a multicomponent quality improvement strategy on sustained achievement of diabetes care goals and macrovascular and microvascular complications in South Asia at 6.5 years follow-up: Post hoc analyses of the CARRS randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Diabetes control is poor globally and leads to burdensome microvascular and macrovascular complications. We aimed to assess post hoc between-group differences in sustained risk factor control and macrovascular and microvascular endpoints at 6.5 years in the Center for cArdiovascular Risk Reduction in South Asia (CARRS) randomized trial.
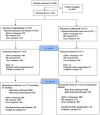
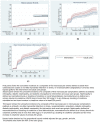
Methods and findings: This parallel group individual randomized clinical trial was performed at 10 outpatient diabetes clinics in India and Pakistan from January 2011 through September 2019. A total of 1,146 patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes (HbA1c ≥8% and systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg and/or LDL-cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL) were randomized to a multicomponent quality improvement (QI) strategy (trained nonphysician care coordinator to facilitate care for patients and clinical decision support system for physicians) or usual care. At 2.5 years, compared to usual care, those receiving the QI strategy were significantly more likely to achieve multiple risk factor control. Six clinics continued, while 4 clinics discontinued implementing the QI strategy for an additional 4-year follow-up (overall median 6.5 years follow-up). In this post hoc analysis, using intention-to-treat, we examined between-group differences in multiple risk factor control (HbA1c <7% plus BP <130/80 mm Hg and/or LDL-cholesterol <100 mg/dL) and first macrovascular endpoints (nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, death, revascularization [angioplasty or coronary artery bypass graft]), which were co-primary outcomes. We also examined secondary outcomes, namely, single risk factor control, first microvascular endpoints (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy), and composite first macrovascular plus microvascular events (which also included amputation and all-cause mortality) by treatment group and whether QI strategy implementation was continued over 6.5 years. At 6.5 years, assessment data were available for 854 participants (74.5%; n = 417 [intervention]; n = 437 [usual care]). In terms of sociodemographic and clinical characteristics, participants in the intervention and usual care groups were similar and participants at sites that continued were no different to participants at sites that discontinued intervention implementation. Patients in the intervention arm were more likely to exhibit sustained multiple risk factor control than usual care (relative risk: 1.77; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.45, 2.16), p < 0.001. Cumulatively, there were 233 (40.5%) first microvascular and macrovascular events in intervention and 274 (48.0%) in usual care patients (absolute risk reduction: 7.5% [95% CI: -13.2, -1.7], p = 0.01; hazard ratio [HR] = 0.72 [95% CI: 0.61, 0.86]), p < 0.001. Patients in the intervention arm experienced lower incidence of first microvascular endpoints (HR = 0.68 [95% CI: 0.56, 0.83), p < 0.001, but there was no evidence of between-group differences in first macrovascular events. Beneficial effects on microvascular and composite vascular outcomes were observed in sites that continued, but not sites that discontinued the intervention.
Conclusions: In urban South Asian clinics, a multicomponent QI strategy led to sustained multiple risk factor control and between-group differences in microvascular, but not macrovascular, endpoints. Between-group reductions in vascular outcomes at 6.5 years were observed only at sites that continued the QI intervention, suggesting that practice change needs to be maintained for better population health of people with diabetes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01212328.
Copyright: © 2024 Ali et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: MKA has received research support (to Emory University) from Merck and consulting fees from Bayer and Eli Lilly, all outside the scope of this work. SP received research funding in the area of CVD implementation sciences. All other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels, Belgium. 2021 [cited 2022 Feb 1]. https://diabetesatlas.org/.
-
- Saeedi P, Salpea P, Karuranga S, Petersohn I, Malanda B, Gregg EW, et al.. Mortality attributable to diabetes in 20–79 year old adults, 2019 estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162:108086. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108086 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Turnbull F, Neal B, Algert C, Chalmers J, Chapman N, Cutler J, et al.. Effects of Different Blood Pressure-Lowering Regimens on Major Cardiovascular Events in Individuals With and Without Diabetes Mellitus: Results of Prospectively Designed Overviews of Randomized Trials. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(12):1410–1419. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.12.1410 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Collins R, Keech A, Simes J, Peto R, et al.. Efficacy of cholesterol-lowering therapy in 18,686 people with diabetes in 14 randomised trials of statins: a meta-analysis. Lancet (London, England). 2008;371(9607):117–125. Epub 2008/01/15. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60104-X . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

