Epitranscriptomic cytidine methylation of the hepatitis B viral RNA is essential for viral reverse transcription and particle production
- PMID: 38830096
- PMCID: PMC11181118
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2400378121
Epitranscriptomic cytidine methylation of the hepatitis B viral RNA is essential for viral reverse transcription and particle production
Abstract
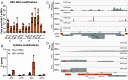
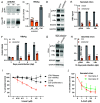
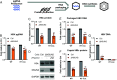
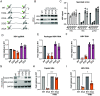
Epitranscriptomic RNA modifications have emerged as important regulators of the fate and function of viral RNAs. One prominent modification, the cytidine methylation 5-methylcytidine (m5C), is found on the RNA of HIV-1, where m5C enhances the translation of HIV-1 RNA. However, whether m5C functionally enhances the RNA of other pathogenic viruses remains elusive. Here, we surveyed a panel of commonly found RNA modifications on the RNA of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and found that HBV RNA is enriched with m5C as well as ten other modifications, at stoichiometries much higher than host messenger RNA (mRNA). Intriguingly, m5C is mostly found on the epsilon hairpin, an RNA element required for viral RNA encapsidation and reverse transcription, with these m5C mainly deposited by the cellular methyltransferase NSUN2. Loss of m5C from HBV RNA due to NSUN2 depletion resulted in a partial decrease in viral core protein (HBc) production, accompanied by a near-complete loss of the reverse transcribed viral DNA. Similarly, mutations introduced to remove the methylated cytidines resulted in a loss of HBc production and reverse transcription. Furthermore, pharmacological disruption of m5C deposition led to a significant decrease in HBV replication. Thus, our data indicate m5C methylations as a critical mediator of the epsilon elements' function in HBV virion production and reverse transcription, suggesting the therapeutic potential of targeting the m5C methyltransfer process on HBV epsilon as an antiviral strategy.
Keywords: NSUN2; RNA modifications; hepatitis B virus; m5C; reverse transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

