Bispecific antibodies targeting two glycoproteins on SFTSV exhibit synergistic neutralization and protection in a mouse model
- PMID: 38830098
- PMCID: PMC11181109
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2400163121
Bispecific antibodies targeting two glycoproteins on SFTSV exhibit synergistic neutralization and protection in a mouse model
Abstract
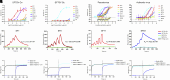
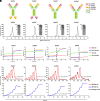
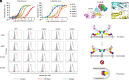
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging infectious disease with a high fatality rate of up to 30% caused by SFTS virus (SFTSV). However, no specific vaccine or antiviral therapy has been approved for clinical use. To develop an effective treatment, we isolated a panel of human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). SF5 and SF83 are two neutralizing mAbs that recognize two viral glycoproteins (Gn and Gc), respectively. We found that their epitopes are closely located, and we then engineered them as several bispecific antibodies (bsAbs). Neutralization and animal experiments indicated that bsAbs display more potent protective effects than the parental mAbs, and the cryoelectron microscopy structure of a bsAb3 Fab-Gn-Gc complex elucidated the mechanism of protection. In vivo virus passage in the presence of antibodies indicated that two bsAbs resulted in less selective pressure and could efficiently bind to all single parental mAb-escape mutants. Furthermore, epitope analysis of the protective mAbs against SFTSV and RVFV indicated that they are all located on the Gn subdomain I, where may be the hot spots in the phleboviruses. Collectively, these data provide potential therapeutic agents and molecular basis for the rational design of vaccines against SFTSV infection.
Keywords: SFTSV; bispecific antibody; bunyavirus; glycoproteins; structural basis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:Z. Chang, D.G., F.G., and Y.W. are listed as inventors on two pending patent applications. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Liu Q., He B., Huang S. Y., Wei F., Zhu X. Q., Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 14, 763–772 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Liu W., et al. , Case-fatality ratio and effectiveness of ribavirin therapy among hospitalized patients in china who had severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 57, 1292–1299 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32090014/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 82022042/MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC)
- 2022YFC2303402/MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China (NKPs)
- 2020YFA0907104/MOST | National Key Research and Development Program of China (NKPs)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

