Factor analysis of lifetime psychopathology and its brain morphometric and genetic correlates in a transdiagnostic sample
- PMID: 38830892
- PMCID: PMC11148082
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-02936-6
Factor analysis of lifetime psychopathology and its brain morphometric and genetic correlates in a transdiagnostic sample
Abstract
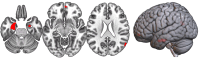
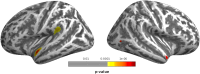
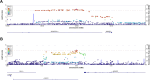
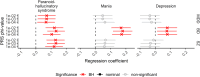
There is a lack of knowledge regarding the relationship between proneness to dimensional psychopathological syndromes and the underlying pathogenesis across major psychiatric disorders, i.e., Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), Bipolar Disorder (BD), Schizoaffective Disorder (SZA), and Schizophrenia (SZ). Lifetime psychopathology was assessed using the OPerational CRITeria (OPCRIT) system in 1,038 patients meeting DSM-IV-TR criteria for MDD, BD, SZ, or SZA. The cohort was split into two samples for exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. All patients were scanned with 3-T MRI, and data was analyzed with the CAT-12 toolbox in SPM12. Psychopathological factor scores were correlated with gray matter volume (GMV) and cortical thickness (CT). Finally, factor scores were used for exploratory genetic analyses including genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and polygenic risk score (PRS) association analyses. Three factors (paranoid-hallucinatory syndrome, PHS; mania, MA; depression, DEP) were identified and cross-validated. PHS was negatively correlated with four GMV clusters comprising parts of the hippocampus, amygdala, angular, middle occipital, and middle frontal gyri. PHS was also negatively associated with the bilateral superior temporal, left parietal operculum, and right angular gyrus CT. No significant brain correlates were observed for the two other psychopathological factors. We identified genome-wide significant associations for MA and DEP. PRS for MDD and SZ showed a positive effect on PHS, while PRS for BD showed a positive effect on all three factors. This study investigated the relationship of lifetime psychopathological factors and brain morphometric and genetic markers. Results highlight the need for dimensional approaches, overcoming the limitations of the current psychiatric nosology.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Psychopathological Syndromes Across Affective and Psychotic Disorders Correlate With Gray Matter Volumes.Schizophr Bull. 2021 Oct 21;47(6):1740-1750. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbab037. Schizophr Bull. 2021. PMID: 33860786 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic contributions to transdiagnostic symptom dimensions in patients with major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia spectrum disorders.Schizophr Res. 2023 Feb;252:161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Schizophr Res. 2023. PMID: 36652833
-
Pattern recognition of magnetic resonance imaging-based gray matter volume measurements classifies bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder.J Affect Disord. 2018 Feb;227:498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.11.043. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29156364 Free PMC article.
-
Gray matter alterations in adolescent major depressive disorder and adolescent bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2023 Mar 15;325:550-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.01.049. Epub 2023 Jan 17. J Affect Disord. 2023. PMID: 36669567 Review.
-
Asymmetrical alterations of grey matter among psychiatric disorders: A systematic analysis by voxel-based activation likelihood estimation.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 30;110:110322. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110322. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33838150
References
-
- Wong TY, Radua J, Pomarol-Clotet E, Salvador R, Albajes-Eizagirre A, Solanes A et al. An overlapping pattern of cerebral cortical thinning is associated with both positive symptoms and aggression in schizophrenia via the ENIGMA consortium. Psychol Med. 2020;50:2034–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- KR 3822/5-1, KR 3822/7-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- NE 2254/1-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- DA 1151/5-1, DA 1151/5-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- KI 588/14-1, KI 588/14-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

