Nurturing gut health: role of m6A RNA methylation in upholding the intestinal barrier
- PMID: 38830900
- PMCID: PMC11148167
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-024-02043-x
Nurturing gut health: role of m6A RNA methylation in upholding the intestinal barrier
Abstract
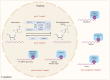
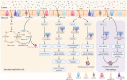
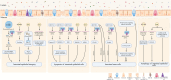
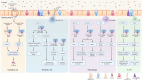
The intestinal lumen acts as a critical interface connecting the external environment with the body's internal state. It's essential to prevent the passage of harmful antigens and bacteria while facilitating nutrient and water absorption. The intestinal barriers encompass microbial, mechanical, immunological, and chemical elements, working together to maintain intestinal balance. Numerous studies have associated m6A modification with intestinal homeostasis. This review comprehensively outlines potential mechanisms through which m6A modification could initiate, exacerbate, or sustain barrier damage from an intestinal perspective. The pivotal role of m6A modification in preserving intestinal equilibrium provides new insights, guiding the exploration of m6A modification as a target for optimizing preventive and therapeutic strategies for intestinal homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
m6A modification in inflammatory bowel disease provides new insights into clinical applications.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114298. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114298. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36706633 Review.
-
New insights into the intestinal barrier through "gut-organ" axes and a glimpse of the microgravity's effects on intestinal barrier.Front Physiol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1465649. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1465649. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39450142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roseburia intestinalis Supplementation Could Reverse the Learning and Memory Impairment and m6A Methylation Modification Decrease Caused by 27-Hydroxycholesterol in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 26;16(9):1288. doi: 10.3390/nu16091288. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38732535 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in platinum resistance.Epigenomics. 2023 Nov;15(22):1221-1232. doi: 10.2217/epi-2023-0289. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Epigenomics. 2023. PMID: 38009226 Review.
-
Novel insights into the interaction between N6-methyladenosine methylation and noncoding RNAs in musculoskeletal disorders.Cell Prolif. 2022 Oct;55(10):e13294. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13294. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 35735243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
M6A RNA modification: focusing on non-small cell lung cancer progression, therapeutic strategies and challenges.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 16;15:1622359. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1622359. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40740874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of m6A RNA methylation and gut microbiota in modulating gut injury.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2467213. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2467213. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39960310 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

