Epidemiological trends, antifungal drug susceptibility and SQLE point mutations in etiologic species of human dermatophytosis in Al-Diwaneyah, Iraq
- PMID: 38830918
- PMCID: PMC11148054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-63425-w
Epidemiological trends, antifungal drug susceptibility and SQLE point mutations in etiologic species of human dermatophytosis in Al-Diwaneyah, Iraq
Abstract
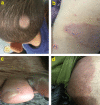
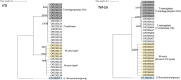
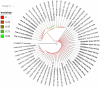
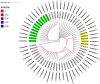
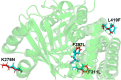
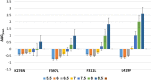
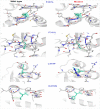
Dermatophytes show a wide geographic distribution and are the main causative agents of skin fungal infections in many regions of the world. Recently, their resistance to antifungal drugs has led to an obstacle to effective treatment. To address the lack of dermatophytosis data in Iraq, this study was designed to investigate the distribution and prevalence of dermatophytes in the human population and single point mutations in squalene epoxidase gene (SQLE) of terbinafine resistant isolates. The identification of 102 dermatophytes isolated from clinical human dermatophytosis was performed through morphological and microscopic characteristics followed by molecular analysis based on ITS and TEF-1α sequencing. Phylogeny was achieved through RAxML analysis. CLSI M38-A2 protocol was used to assess antifungal susceptibility of the isolates to four major antifungal drugs. Additionally, the presence of point mutations in SQLE gene, which are responsible for terbinafine resistance was investigated. Tinea corporis was the most prevalent clinical manifestation accounting for 37.24% of examined cases of dermatophytosis. Based on ITS, T. indotineae (50.98%), T. mentagrophytes (19.61%), and M. canis (29.41%) was identified as an etiologic species. T. indotineae and T. mentagrophytes strains were identified as T. interdigitale based on TEF-1α. Terbinafine showed the highest efficacy among the tested antifungal drugs. T. indotineae and T. mentagrophytes showed the highest resistance to antifungal drugs with MICs of 2-4 and 4 μg/mL, while M. canis was the most susceptible species. Three of T. indotineae isolates showed mutations in SQLE gene Phe397Leu substitution. A non-previously described point mutation, Phe311Leu was identified in T. indotineae and mutations Lys276Asn, Phe397Leu and Leu419Phe were diagnosed in T. mentagrophytes XVII. The results of mutation analysis showed that Phe397Leu was a destabilizing mutation; protein stability has decreased with variations in pH, and point mutations affected the interatomic interaction, resulting in bond disruption. These results could help to control the progression of disease effectively and make decisions regarding the selection of appropriate drugs for dermatophyte infections.
Keywords: SQLE mutation; Antifungal susceptibility; Dermatophytes; Dermatophytosis; Iraq; Terbinafine resistance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High Prevalence of Terbinafine Resistance Among Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale Species Complex, a Cross-Sectional Study from 2021 to 2022 in Northern Parts of Iran.Mycopathologia. 2024 Jun 12;189(4):52. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00855-0. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38864945
-
Increased terbinafine resistance among clinical genotypes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale species complex harboring squalene epoxidase gene mutations.J Mycol Med. 2024 Sep;34(3):101495. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2024.101495. Epub 2024 Jun 16. J Mycol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896927
-
First Reported Cases of Terbinafine-Resistant Trichophyton indotineae Isolates in Israel: Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics and Response to Treatment.Mycoses. 2024 Nov;67(11):e13812. doi: 10.1111/myc.13812. Mycoses. 2024. PMID: 39547945
-
The Emerging Terbinafine-Resistant Trichophyton Epidemic: What Is the Role of Antifungal Susceptibility Testing?Dermatology. 2022;238(1):60-79. doi: 10.1159/000515290. Epub 2021 May 31. Dermatology. 2022. PMID: 34058736 Review.
-
An update on antifungal resistance in dermatophytosis.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024 Apr;25(5):511-519. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2024.2343079. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38623728 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging antifungal resistance in Trichophyton mentagrophytes: insights from susceptibility profiling and genetic mutation analysis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2450026. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2450026. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 39749731 Free PMC article.
-
Terbinafine Resistance in Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton indotineae: A Literature Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 May 7;14(5):472. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14050472. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolving Phylogenetic Relationships Within the Trichophyton mentagrophytes Complex: A RADseq Genomic Approach Challenges Status of 'Terbinafine-Resistant' Trichophyton indotineae as Distinct Species.Mycoses. 2025 Apr;68(4):e70050. doi: 10.1111/myc.70050. Mycoses. 2025. PMID: 40183506 Free PMC article.
-
[Trichophyton mentagrophytes ITS genotype VIII/Trichophyton indotineae in Germany-revisit after 5 years].Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s00105-025-05553-6. Online ahead of print. Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40796670 German.
-
Computational analysis of missense mutations in squalene epoxidase associated with terbinafine resistance in clinically reported dermatophytes.Sci Rep. 2025 May 28;15(1):18612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03300-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40436978 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

