Geographic sources of ozone air pollution and mortality burden in Europe
- PMID: 38830993
- PMCID: PMC11186783
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-02976-x
Geographic sources of ozone air pollution and mortality burden in Europe
Abstract
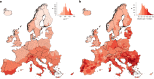
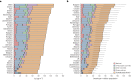
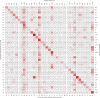
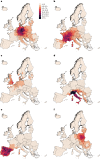
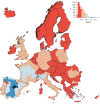
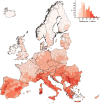
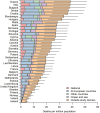
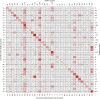
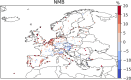
Ground-level ozone (O3) is a harmful air pollutant formed in the atmosphere by the interaction between sunlight and precursor gases. Exposure to current O3 levels in Europe is a major source of premature mortality from air pollution. However, mitigation actions have been mainly designed and implemented at the national and regional scales, lacking a comprehensive assessment of the geographic sources of O3 pollution and its associated health impacts. Here we quantify both national and imported contributions to O3 and their related mortality burden across 813 contiguous regions in 35 European countries, representing about 530 million people. Imported O3 contributed to 88.3% of all O3-attributable deaths (intercountry range 83-100%). The greatest share of imported O3 had its origins outside the study domain (that is, hemispheric sources), which was responsible for 56.7% of total O3-attributable mortality (range 42.5-87.2%). It was concluded that achieving the air-quality guidelines set out by the World Health Organization and avoiding the health impacts of O3 require not only the implementation of national or coordinated pan-European actions but also global strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Air quality in Europe 2020 (European Environment Agency, 2020); www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2020-report
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

