Genetic variants in UNC93B1 predispose to childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 38831104
- PMCID: PMC11147776
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01846-5
Genetic variants in UNC93B1 predispose to childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Genetic variants in UNC93B1 predispose to childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus.Nat Immunol. 2024 Oct;25(10):1977. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01969-9. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39251802 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
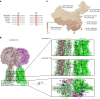
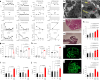
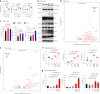
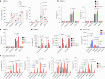
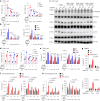
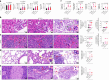
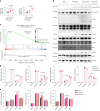
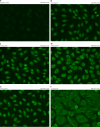
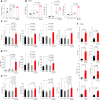
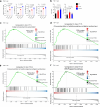
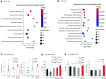
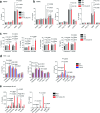
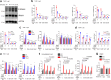
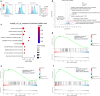
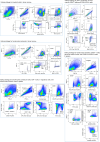
Rare genetic variants in toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) are known to cause lupus in humans and mice. UNC93B1 is a transmembrane protein that regulates TLR7 localization into endosomes. In the present study, we identify two new variants in UNC93B1 (T314A, located proximally to the TLR7 transmembrane domain, and V117L) in a cohort of east Asian patients with childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. The V117L variant was associated with increased expression of type I interferons and NF-κB-dependent cytokines in patient plasma and immortalized B cells. THP-1 cells expressing the variant UNC93B1 alleles exhibited exaggerated responses to stimulation of TLR7/-8, but not TLR3 or TLR9, which could be inhibited by targeting the downstream signaling molecules, IRAK1/-4. Heterozygous mice expressing the orthologous Unc93b1V117L variant developed a spontaneous lupus-like disease that was more severe in homozygotes and again hyperresponsive to TLR7 stimulation. Together, this work formally identifies genetic variants in UNC93B1 that can predispose to childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.L.M. is a scientific advisor for Odyssey therapeutics and NRG therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81873869/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32250410295/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82101911/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82125015/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

