Association between oxidative balance score and kidney stones: data from the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES)
- PMID: 38831279
- PMCID: PMC11149272
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03607-w
Association between oxidative balance score and kidney stones: data from the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES)
Abstract
Purpose: Some studies have found that the pathological formation of kidney stones is closely related to injury and inflammatory response. Behaviors such as dietary composition, physical activity, obesity and smoking can all affect the body's oxidative stress levels. In order to evaluate the effects of various diets and lifestyles on the body's oxidative and antioxidant systems, an oxidative balance score was developed. To investigate whether the OBS is associated with the development of kidney stones.
Methods: Data were taken from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2007-2018, followed by retrospective observational studies. The association between kidney stones and OBS was analyzed using survey-weighted logistic regression by adjusting for demographics, laboratory tests, and medical comorbidity covariates. The oxidative balance score is calculated by screening 16 nutrients and 4 lifestyle factors, including 5 prooxidants and 15 antioxidants, based on prior information about the relationship between oxidation levels in the body and nutrients or lifestyle factors.
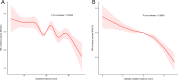
Results: A total of 26,786 adult participants were included in the study, of which 2,578, or 9.62%, had a history of nephrolithiasis. Weighted logistic regression analysis found an association between OBS and kidney stones. In the fully tuned model, i.e., model 3, the highest quartile array of OBS was associated with the lowest quartile array of OBS (OR = 0.73 (0.57, 0.92)) with the risk of kidney stone (p = 0.01), and was statistically significant and remained relatively stable in each model. At the same time, the trend test in the model is also statistically significant. With the increase of OBS, the OR value of kidney stones generally tends to decrease.
Conclusions: There is an inverse correlation between OBS and kidney stone disease. At the same time, higher OBS suggests that antioxidant exposure is greater than pro-oxidative exposure in diet and lifestyle, and is associated with a lower risk of kidney stones.
Keywords: Kidney stones; National health and nutrition examination survey; Oxidative balance score; Reactive oxygen species; Restricted cubic spline regression analysis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources