Fertility-sparing uterine displacement for pelvic malignancies: surgical options and radiotherapy dosimetry on a human cadaver
- PMID: 38831328
- PMCID: PMC11145884
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-024-03423-4
Fertility-sparing uterine displacement for pelvic malignancies: surgical options and radiotherapy dosimetry on a human cadaver
Abstract
Background: Radio(chemo)therapy is often required in pelvic malignancies (cancer of the anus, rectum, cervix). Direct irradiation adversely affects ovarian and endometrial function, compromising the fertility of women. While ovarian transposition is an established method to move the ovaries away from the radiation field, surgical procedures to displace the uterus are investigational. This study demonstrates the surgical options for uterine displacement in relation to the radiation dose received. METHODS: The uterine displacement techniques were carried out sequentially in a human female cadaver to demonstrate each procedure step by step and assess the uterine positions with dosimetric CT scans in a hybrid operating room. Two treatment plans (anal and rectal cancer) were simulated on each of the four dosimetric scans (1. anatomical position, 2. uterine suspension of the round ligaments to the abdominal wall 3. ventrofixation of the uterine fundus at the umbilical level, 4. uterine transposition). Treatments were planned on Eclipse® System (Varian Medical Systems®,USA) using Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy. Data about maximum (Dmax) and mean (Dmean) radiation dose received and the volume receiving 14 Gy (V14Gy) were collected.
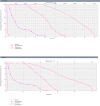
Results: All procedures were completed without technical complications. In the rectal cancer simulation with delivery of 50 Gy to the tumor, Dmax, Dmean and V14Gy to the uterus were respectively 52,8 Gy, 34,3 Gy and 30,5cc (1), 31,8 Gy, 20,2 Gy and 22.0cc (2), 24,4 Gy, 6,8 Gy and 5,5cc (3), 1,8 Gy, 0,6 Gy and 0,0cc (4). For anal cancer, delivering 64 Gy to the tumor respectively 46,7 Gy, 34,8 Gy and 31,3cc (1), 34,3 Gy, 20,0 Gy and 21,5cc (2), 21,8 Gy, 5,9 Gy and 2,6cc (3), 1,4 Gy, 0,7 Gy and 0,0cc (4).
Conclusions: The feasibility of several uterine displacement procedures was safely demonstrated. Increasing distance to the radiation field requires more complex surgical interventions to minimize radiation exposure. Surgical strategy needs to be tailored to the multidisciplinary treatment plan, and uterine transposition is the most technically complex with the least dose received.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer today [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 23]. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- Pavone M, Goglia M, Scambia G, Querleu D, Akladios C, Lecointre L. Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal trachelectomy with prophylactic cerclage: a safe fertility-sparing treatment for early stage cervical Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024;31(3):1804–5. - PubMed
-
- Mathews TJ, Hamilton BE. Mean Age of Mothers is on the rise: United States, 2000–2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2016;(232):1–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources