A systematic review and meta-analysis of systematic and topical tranexamic acid administration in aesthetic plastic surgery
- PMID: 38831387
- PMCID: PMC11149283
- DOI: 10.1186/s13741-024-00406-7
A systematic review and meta-analysis of systematic and topical tranexamic acid administration in aesthetic plastic surgery
Abstract
Introduction: Tranexamic acid has been widely used in plastic surgery. However, its efficacy has yet to be fully established. This meta-analysis aimed to determine its effectiveness in aesthetic plastic surgery.
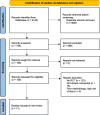
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, we conducted a meta-analysis of prospective randomised clinical trials that compared the effects of topical or systematic administration of tranexamic acid versus the control group in aesthetic plastic surgeries. The study was registered on the International Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) and is available online ( www.crd.york.uk/prospero , CRD42023492585).
Results: Eleven studies encompassing 960 patients were included for the synthesis after critical evaluation. Systematic (MD - 18.05, 95% Cl, - 22.01, - 14.09, p < 0.00001) and topical (MD - 74.93, 95% Cl, - 88.79, - 61.07, p < 0.00001) administration of tranexamic acid reduced total blood loss. Topical tranexamic acid reduced drainage output (p < 0.0006).
Conclusion: Tranexamic acid reduced blood loss in aesthetic plastic surgery. More strictly defined RCTs, using high-quality methodology, are needed to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of tranexamic acid in aesthetic plastic surgery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Role of Tranexamic Acid in Plastic Surgery: a Systematic Review].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2023 Aug;55(4):304-314. doi: 10.1055/a-2082-1813. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2023. PMID: 37473772 German.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 Jan 19;12(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0512-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28103911 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Impact of Tranexamic Acid Administration in Aesthetic Plastic Surgery.Aesthet Surg J. 2022 Apr 12;42(5):548-558. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjab333. Aesthet Surg J. 2022. PMID: 34486647
-
Evaluation of the Safety and Effectiveness of Topical Intrapleural Application of Tranexamic Acid in Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296231218215. doi: 10.1177/10760296231218215. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 38115686 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intravenous versus topical tranexamic acid in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: An updated meta-analysis.Thromb Res. 2017 May;153:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Thromb Res. 2017. PMID: 28319822 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreasing Venous Thromboembolism With Anticoagulation in Plastic Surgery.Plast Surg (Oakv). 2025 Jan 31:22925503251315490. doi: 10.1177/22925503251315490. Online ahead of print. Plast Surg (Oakv). 2025. PMID: 39898339 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Late-Onset Pneumothorax and Bilateral Pulmonary Embolism Following Combined Liposuction and Mastopexy: A Case Report and Literature Review.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2025 Jun 14;7:ojaf062. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojaf062. eCollection 2025. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2025. PMID: 40704042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badireddy M, Mudipalli VR. Deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis. 2018. - PubMed
-
- Beikaei M, Ghazipour A, Derakhshande V, Saki N, Nikakhlagh S. Evaluating the effect of intravenous tranexamic acid on intraoperative bleeding during elective rhinoplasty surgery. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2015;8:723–759. doi: 10.13005/bpj/779. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources