Stress reduction through taiji: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38831412
- PMCID: PMC11149313
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-024-04493-3
Stress reduction through taiji: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: In light of the mounting prevalence of stress in contemporary society and the growing interest in stress reduction methods, this review investigates the potential of taiji as a viable strategy for alleviating stress.
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (CENTRAL), PsycINFO, and Web of Science were searched up to April 2023 to identify randomized controlled trials of taiji. Studies in both patients and healthy populations were considered. They had to provide a measure of perceived stress and include a no treatment or placebo control group. Data were extracted by two reviewers. Pooled standardized mean differences (SMD) were calculated for perceived stress, biological stress markers, anxiety, depression, and quality of life (QoL). Meta-regression analyses were performed to identify sources of heterogeneity.
Results: Eleven trials with a total of 1323 patients comparing taiji to no intervention met the inclusion criteria. The included studies varied strongly with regard to patient characteristics, taiji intervention, and methodological quality. The overall SMD for perceived stress was significant at -0.41 (95% confidence interval, CI, -0.63 to -0.19; I2 = 63%). Exclusion of studies with less than 100 participants yielded a diminished SMD at -0.26 (95% CI, -0.45 to -0.06). The SMD for perceived stress at follow-up was significant (-0.25, 95% CI -0.46 to -0.05). Secondary outcomes highlighted improvements in anxiety and physical QoL, while depression, mental QoL, and biological stress markers remained unchanged.
Conclusions: Results underscore taiji's potential in mitigating perceived stress in both patients and healthy populations, paralleled by enhancements in depressive symptoms, anxiety levels, and physical QoL.
Keywords: Evidence-based practice; Mind–body exercise; Relaxation; Stress reduction; Tai Chi.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


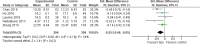
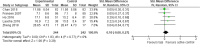



Similar articles
-
Mindfulness-based stress reduction for women diagnosed with breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 27;3(3):CD011518. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011518.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30916356 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) on symptom variables and health-related quality of life in breast cancer patients-a systematic review and meta-analysis.Support Care Cancer. 2019 Mar;27(3):771-781. doi: 10.1007/s00520-018-4570-x. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Support Care Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30488223
-
The effect of tai chi and Qigong exercise on depression and anxiety of individuals with substance use disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 May 29;20(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02967-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32471415 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 2;12(12):CD004542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31789430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The influence of traditional Chinese exercise on brain function compared with other sports: A meta-analysis on functional neuroimaging studies.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 23;10(17):e36736. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36736. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281439 Free PMC article.
-
Mind-Body Medicine in the Treatment of Depression: A Narrative Review of Efficacy, Safety and Mechanisms.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024 Dec;26(12):729-740. doi: 10.1007/s11920-024-01548-7. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024. PMID: 39424743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang G, Li W, Klupp N, Cao H, Liu J, Bensoussan A, et al. Does tai chi improve psychological well-being and quality of life in patients with cardiovascular disease and/or cardiovascular risk factors? A systematic review. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022;22:3. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03482-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

