Treatment planning for MR-guided SBRT of pancreatic tumors on a 1.5 T MR-Linac: A global consensus protocol
- PMID: 38831754
- PMCID: PMC11145226
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100797
Treatment planning for MR-guided SBRT of pancreatic tumors on a 1.5 T MR-Linac: A global consensus protocol
Abstract
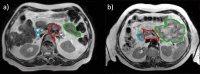
Background and purpose: Treatment planning for MR-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for pancreatic tumors can be challenging, leading to a wide variation of protocols and practices. This study aimed to harmonize treatment planning by developing a consensus planning protocol for MR-guided pancreas SBRT on a 1.5 T MR-Linac.
Materials and methods: A consortium was founded of thirteen centers that treat pancreatic tumors on a 1.5 T MR-Linac. A phased planning exercise was conducted in which centers iteratively created treatment plans for two cases of pancreatic cancer. Each phase was followed by a meeting where the instructions for the next phase were determined. After three phases, a consensus protocol was reached.
Results: In the benchmarking phase (phase I), substantial variation between the SBRT protocols became apparent (for example, the gross tumor volume (GTV) D99% ranged between 36.8 - 53.7 Gy for case 1, 22.6 - 35.5 Gy for case 2). The next phase involved planning according to the same basic dosimetric objectives, constraints, and planning margins (phase II), which led to a large degree of harmonization (GTV D99% range: 47.9-53.6 Gy for case 1, 33.9-36.6 Gy for case 2). In phase III, the final consensus protocol was formulated in a treatment planning system template and again used for treatment planning. This not only resulted in further dosimetric harmonization (GTV D99% range: 48.2-50.9 Gy for case 1, 33.5-36.0 Gy for case 2) but also in less variation of estimated treatment delivery times.
Conclusion: A global consensus protocol has been developed for treatment planning for MR-guided pancreatic SBRT on a 1.5 T MR-Linac. Aside from harmonizing the large variation in the current clinical practice, this protocol can provide a starting point for centers that are planning to treat pancreatic tumors on MR-Linac systems.
Keywords: Consensus protocol; MR-guided SBRT; Pancreatic cancer; Treatment planning.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Parikh P.J., Lee P., Low D.A., Kim J., Mittauer K.E., Bassetti M.F., et al. A multi-institutional phase II trial of ablative 5-fraction stereotactic MR-guided on-table adaptive radiation therapy for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023;117(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.05.023. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

