Role of TIM-1 in the development and treatment of tumours
- PMID: 38831760
- PMCID: PMC11144867
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1307806
Role of TIM-1 in the development and treatment of tumours
Abstract
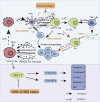
T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin structural domain 1 (TIM-1, also known as hepatitis A virus cell receptor 1) is a co-stimulatory molecule that is expressed predominantly on the surface of T cells. TIM-1 promotes the activation and proliferation of T cells, cytokine secretion, and can also be overexpressed in various types of cancer. Upregulation of TIM-1 expression may be associated with the development and progression of cancer. After reviewing the literature, we propose that TIM-1 affects tumour development mainly through two pathways. In the Direct pathway: overexpression in tumours activates tumour-related signaling pathways, mediates the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis, and directly affects tumour development directly. In the indirect pathway: In addition to changing the tumour microenvironment and influencing the growth of tumours, TIM-1 binds to ligands to encourage the activation, proliferation, and generation of cytokines by immune cells. This review examines how TIM-1 stimulates the development of tumours in direct and indirect ways, and how TIM-1 is exploited as a target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: TIM-1; target; the tumour microenvironment; therapy; tumour.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Qing, Zhu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

