Oral Prostacyclin Pathway Agents Used in PAH: A Targeted Literature Review
- PMID: 38831921
- PMCID: PMC11146608
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S460912
Oral Prostacyclin Pathway Agents Used in PAH: A Targeted Literature Review
Abstract
Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare and progressive pulmonary vascular disease that can result in right heart failure and death. Oral prostacyclins play an important role in the management of intermediate-low risk PAH. This targeted literature review (TLR) aimed to identify and compare evidence supporting use of oral prostacyclin pathway agents (PPAs: selexipag and oral treprostinil) in intermediate-low risk PAH.
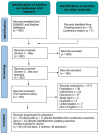
Methods: A targeted literature review was conducted. Literature databases (MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane reviews) were searched for studies describing clinical practice and treatment outcomes for oral treprostinil and selexipag globally, published in English (2012 to 2022). Electronic searches were supplemented by manual-searches of targeted conferences (2020 to 2022), and reference lists of identified publications were reviewed. One reviewer assessed studies for eligibility.
Results: In total, 95 publications met inclusion criteria: 47 full-text articles (selexipag n = 22; oral treprostinil n = 16; selexipag and oral treprostinil n = 9) and 48 conference materials. Selexipag and oral treprostinil target the prostacyclin pathway differently; their label-supporting trials had different primary endpoints (disease progression and hospitalization vs exercise capacity and disease progression), differing baseline therapy (0, 1 or 2 vs 0 or 1 baseline treatments), titration duration and dosing (personalized dose capped at 1600 ug twice daily (BID) vs increasing doses over time with no maximum dose), respectively. While both oral PPAs have demonstrated reduced risk of disease progression, only selexipag showed reduction in hospitalization rates. Oral PPAs have been shown to reduce healthcare costs in real-world clinical practice. This difference is reflected in labeled indications.
Conclusion: Given differences in trial- and real-world outcomes, number of prior therapies, and dosing, personalizing the choice of oral PPA is critical to maximizing the benefit for individual patients.
Keywords: outcomes; pulmonary hypertension; selexipag; treprostinil.
Plain language summary
PAH is a condition that causes heart failure. It is important to take medicines to slow down this process. For people with early disease, there are some medicines that can be taken as a tablet rather than as an injection to slow down disease progression. The differences between two of the tablet options – selexipag and oral treprostinil, are unclear. We reviewed publications describing how, when and why these medicines are used and how well they work, to improve our understanding of the value of these medicines to people with PAH.
© 2024 Burger et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Charles Burger reports personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from INSMED, personal fees from Merck, and non-financial support from United Therapeutics, during the conduct of the study. Yuen Tsang is a former employee and owns stock in Johnson & Johnson. Dr Marie Chivers, Nikki Atkins and Ms Riya Vekaria report employment with Avalere Health which was in receipt of payment from Janssen for this element of the study. Dr Gurinderpal Doad and Dr Sumeet Panjabi are employees and stockholders of Johnson & Johnson, the company that markets oral selexipag. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of costs and healthcare resource utilization of oral selexipag versus inhaled treprostinil or oral treprostinil in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Med Econ. 2023 Jan-Dec;26(1):644-655. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2204769. J Med Econ. 2023. PMID: 37086091
-
Safety and efficacy of transitioning from selexipag to oral treprostinil in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Findings from the ADAPT registry.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Oct;82:102232. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102232. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37451609
-
Prostacyclin for pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 May 1;5(5):CD012785. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012785.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31042010 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and tolerability of transition from inhaled treprostinil to oral selexipag in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results from the TRANSIT-1 study.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019 Jan;38(1):43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 12. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30391194 Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Intravenous Selexipag in Managing PAH and Bridging Gaps in Oral Treatment: A Narrative Review.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025 Jan 10;21:55-60. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S332358. eCollection 2025. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2025. PMID: 39816668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and pharmacokinetics of ralinepag, a novel oral prostacyclin receptor agonist.JHLT Open. 2025 Apr 23;9:100270. doi: 10.1016/j.jhlto.2025.100270. eCollection 2025 Aug. JHLT Open. 2025. PMID: 40485996 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

