The Validity of Muscle Ultrasound in the Diagnostic Workup of Sarcopenia Among Older Adults: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 38831963
- PMCID: PMC11146336
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S463917
The Validity of Muscle Ultrasound in the Diagnostic Workup of Sarcopenia Among Older Adults: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Purpose: Muscle ultrasound has emerged as a promising method in the diagnostic work-up of sarcopenia. The objective of this scoping review was to explore the validity of muscle ultrasound against the latest sarcopenia definitions among older adults.
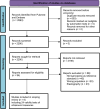
Methods: We adhered to the PRISMA guidelines for scoping reviews. A systematic search of databases was performed by two independent reviewers. All articles comparing the performance of ultrasound to an internationally acknowledged sarcopenia definition among older adults (≥60 years) and published between 2019/01/01 (the year updated sarcopenia definitions were introduced) and 2023/11/15 were included. Data were extracted and collated by muscle and muscle parameters.
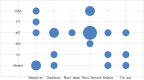
Results: Out of 2290 articles screened, six studies comprising 24 validity tests among a total of 1619 older adults (mean age 74.1 years, 52.2% female) were included. The validity tests investigated the rectus femoris (n = 7), biceps brachii (n = 5), gastrocnemius medialis (n = 4), tibialis anterior (n = 4), soleus (n = 3), and rectus abdominis (n = 1). The parameter muscle thickness (MT) (n = 14) was most commonly measured. The latest European and Asian sarcopenia definitions (EWGSOP2, AWGS2) were applied as reference standards in four validity tests each. None of the studies used the Sarcopenia Definition and Outcome Consortium (SDOC) criteria. The highest area under the curve AUC (0.92, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.89-0.94) was found for the muscle thickness of the rectus femoris muscle. Due to substantial heterogeneity among the studies, pooling of data using a meta-analytic approach was not feasible.
Conclusion: Limited number of studies have examined the validity of muscle ultrasound for diagnosing sarcopenia based on recent definitions among older adults. Thereby, muscle thickness of the rectus femoris showed promising results regarding validity. Further studies are needed to investigate the validity of key muscles and to validate muscle ultrasound among older hospitalized patients.
Keywords: AWGS; EWGSOP; POCUS; SARCUS; SDOC; cross-sectional area; geriatric assessment; muscle thickness; rectus femoris.
© 2024 Staempfli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.