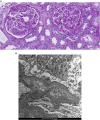
Idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis: a case report
- PMID: 38831990
- PMCID: PMC11144915
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1379547
Idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis: a case report
Abstract
Idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis (ING) is a rare condition characterized by poor renal prognosis. The pathophysiology remains incompletely understood. Histologically, it closely resembles diabetic nephropathy. The development of this disease seems to be influenced by factors such as metabolic syndrome, particularly hypertension and glucose intolerance, along with active smoking. We report a case of ING in an obese 71-year-old male patient who had a long history of untreated hypertension and smoking. The patient underwent conservative treatment involving the administration of an angiotensin-2 receptor antagonist and dapagliflozin, resulting in favorable disease progression. Additional therapeutic measures, such as discontinuation of smoking and efforts toward weight loss, are strongly advised. Furthermore, regular screening for diabetes in the follow-up is crucial, as it can play a pathophysiological role in the disease and may manifest at a later stage, as observed in our clinical case.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; chronic kidney disease; diabetic nephropathy; idiopathic nodular glomerulosclerosis; nephrotic syndrome.
Copyright © 2024 Landry, Rodriguez-Calero, Vogt and Bocchi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alpers CE, Biava CG. Idiopathic lobular glomerulonephritis (nodular mesangial sclerosis): A distinct diagnostic entity. Clin Nephrol. (1989) 32:68–74. - PubMed