Gut Microbiome Alterations Accompany Metabolic Normalization Following Bariatric Surgery in ROHHAD Syndrome
- PMID: 38832003
- PMCID: PMC11146140
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luae091
Gut Microbiome Alterations Accompany Metabolic Normalization Following Bariatric Surgery in ROHHAD Syndrome
Abstract
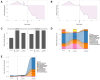
Rapid onset obesity with hypoventilation, hypothalamic, and autonomic dysregulation (ROHHAD) syndrome in childhood is characterized by abrupt onset weight gain and dysautonomia with variable neuroendocrine involvement. In the absence of definitive disease-modifying therapies, the primary management strategy remains symptom control. This case report describes the first successful correction of obesity, dysautonomia, and metabolic derangement in a patient with ROHHAD following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Anthropometrics, metabolic profiling, and stool microbiome composition were assessed in a longitudinal fashion. In the 48-month period following surgery, the patient body mass index (BMI) reduced by 9.5 kg/m2 and metabolic status improved, evidenced in weaning of insulin, and improved glycated hemoglobin, lipid profile, and hepatic enzymes. Chronic diarrhea resolved after surgery and prior to significant weight loss. Evaluation of stool bacterial composition and biomass demonstrated shifts in absolute abundance and taxonomic composition in longitudinal samples following surgery. This case demonstrates the potential efficacy of bariatric surgery in correcting the metabolic disruption of ROHHAD syndrome, producing long-term changes in gut microbiome composition and biomass.
Keywords: ROHHAD; bariatric surgery; gastroenterology; microbiome; obesity.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Harvengt J, Gernay C, Mastouri M, et al. ROHHAD(NET) syndrome: systematic review of the clinical timeline and recommendations for diagnosis and prognosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(7):dgaa247. - PubMed
-
- Hara N, Alkanani AK, Ir D, et al. Prevention of virus-induced type 1 diabetes with antibiotic therapy. J Immunol. 2012;189(8):3805‐3814. - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez-Repiso C, Moreno-Indias I, Tinahones FJ. Shifts in gut microbiota and their metabolites induced by bariatric surgery. Impact of factors shaping gut microbiota on bariatric surgery outcomes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021;22(4):1137‐1156. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
