Immortalized human myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle cell lines to address patient heterogeneity
- PMID: 38832025
- PMCID: PMC11144749
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109930
Immortalized human myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle cell lines to address patient heterogeneity
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Immortalized human myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle cell lines to address patient heterogeneity.iScience. 2024 Dec 9;27(12):111499. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111499. eCollection 2024 Dec 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39735432 Free PMC article.
Abstract
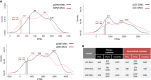
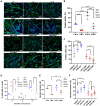
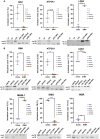
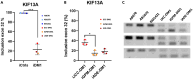
Historically, cellular models have been used as a tool to study myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and the validation of therapies in said pathology. However, there is a need for in vitro models that represent the clinical heterogeneity observed in patients with DM1 that is lacking in classical models. In this study, we immortalized three DM1 muscle lines derived from patients with different DM1 subtypes and clinical backgrounds and characterized them at the genetic, epigenetic, and molecular levels. All three cell lines display DM1 hallmarks, such as the accumulation of RNA foci, MBNL1 sequestration, splicing alterations, and reduced fusion. In addition, alterations in early myogenic markers, myotube diameter and CTCF1 DNA methylation were also found in DM1 cells. Notably, the new lines show a high level of heterogeneity in both the size of the CTG expansion and the aforementioned molecular alterations. Importantly, these immortalized cells also responded to previously tested therapeutics. Altogether, our results show that these three human DM1 cellular models are suitable to study the pathophysiological heterogeneity of DM1 and to test future therapeutic options.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cell biology; Epigenetics; Health sciences; Molecular biology.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bird T. GeneReviews; 1999. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1.
-
- Brook J.D., McCurrach M.E., Harley H.G., Buckler A.J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V.P., Thirion J.P., Hudson T., et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: Expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992;68:799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90154-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

